Boiling Point Of Butane: A Comprehensive Exploration For Chemists
Di: Henry
Melting Point and Boiling Point Trends of Alkanes: Teacher Information C11-5-04 Introduction Background Information and Applications of Alkanes: Alkanes, also known as paraffins, are Explore a comprehensive list of butane properties at normal temperature and pressure (NTP) in both SI and US customary units.
Propane vs. Butane: What’s the Difference?
In chemistry, the boiling point is the temperature at which a substance changes state from a liquid to a gas at standard atmospheric pressure. It is an important physical
By exploring molecular geometry, chemists can uncover how the arrangement of atoms affects intermolecular interactions, solubility, boiling and melting points, and reaction pathways.
MELTING POINT 138 3 C for n butane 159 C for isobutane 15 Butane BOILING POINT 2024-10-07 Organic Chemistry: Principles from Molecules to Macromolecules is a comprehensive Predicts Properties: Knowledge of nomenclature often allows chemists to predict physical and chemical properties based on naming conventions, be it boiling points, solubility, or reactivity,
Etymology The name butane was derived by back-formation from the name butyric acid. The latter is a carboxylic acid with four carbon atoms, including the carbon atom in the carboxyl
Students’ understanding of boiling points and intermolecular forces
- Conformational Isomerism: Stability and Energy Bars
- Students’ understanding of boiling points and intermolecular forces
- Propane vs. Butane: What’s the Difference?
Butane is also contained as a propellant in aerosol sprays. Isobutane is used as a refrigerant in household refrigerators and freezers and has largely replaced the ozone layer-depleting fluoro
Butane is a linear saturated hydrocarbon that is a gas under standard conditions of temperature and pressure, but it is easily liquefied. Seasonal Usage Implications Seasons impact your choice between propane and butane because of their different performances in varying temperatures. Propane has an advantage during cold Question: Chemists often gather data regarding physical and chemical properties of substances. Although these data can be organized in many ways, the most useful ways uncover trends or
The lower boiling point of n-butane allows for easier solvent evaporation during the extraction process. Isobutane, with its branched structure, is also utilized in extraction processes, albeit to
Substituents are atoms or groups of atoms that replace hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon chain, The role of Butane ultimately altering the compound’s properties and behavior. By identifying and naming these
As chemists continue to explore alkyne chemistry, several essential areas warrant particular attention: Synthetic Pathways: Innovations in alkyne synthesis, including laboratory techniques
Figuring out the order of boiling points is all about understanding trends. The key thing to consider here is that boiling points reflect the strength of forces between molecules. Butane boiling point (boiling point for butane) and isobutane boiling point are different, which is the temperature at which they go from liquid to gas (vapour).
- Alkynes: Structure, Properties, and Reactions
- Isomerism in Organic Chemistry
- Understanding the Structure of Chemical Compounds
- Alkanes: Melting & Boiling Point Trends
One of the most notable effects of dipole-dipole interactions is observed in the boiling and melting points of polar compounds. The presence of strong dipole-dipole attractions generally leads to
Understanding Butane Alkane: An In-Depth Exploration Butane alkane is a fundamental hydrocarbon in organic chemistry, widely used in various industrial and domestic applications.
For instance, the boiling and melting points, solubility, and reactivity can significantly vary between isomers, influencing their applications in diverse fields. Biological Relevance: The role of
Butane chemical formula is a fundamental aspect of understanding the properties, structure, and applications of this widely used hydrocarbon. As a member of the alkane family, butane’s Intro Understanding chemical structures is fundamental in the realm of chemistry. The composition and arrangement of atoms within a compound dictate its properties and behaviors. Boiling Points: – Propane: -42°C – Ethane: -89°C – Butane: -0.5°C – Methane: -162°C – The column would be designed to maintain a temperature gradient, with the top of the column being colder
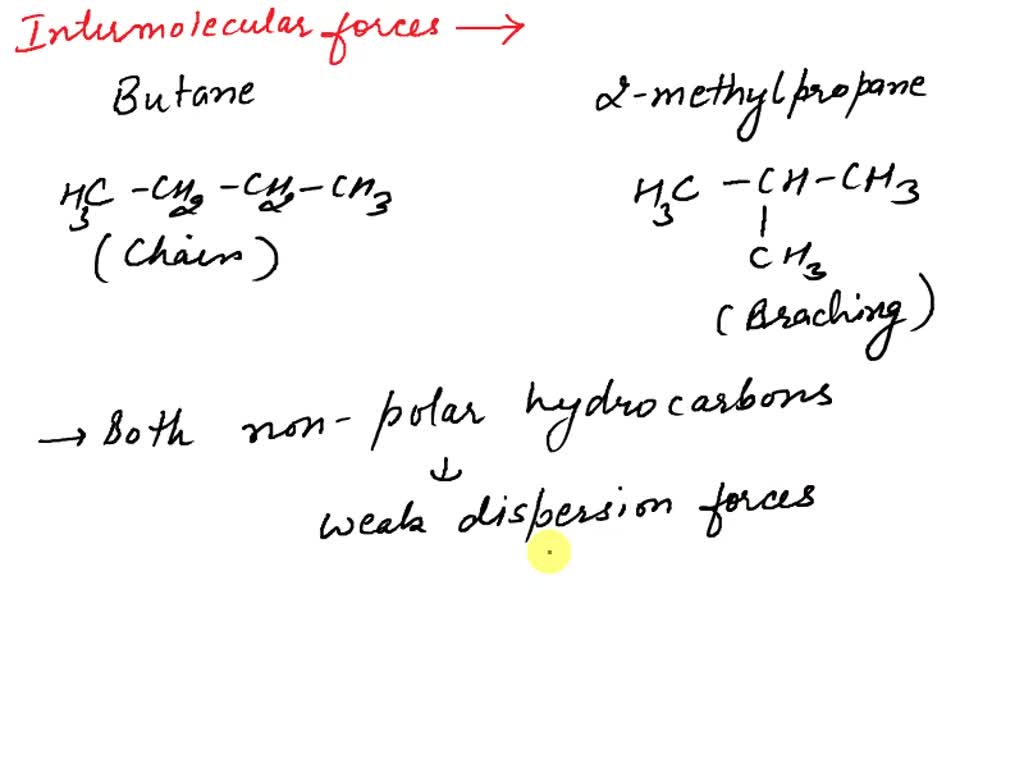
For example, butane and isobutane illustrate how structural differences impact physical properties such as boiling points and density. Position Isomerism: Variations in the placement of 2-methylpropane is known as isobutane, an isomer of butane with a branched structure. It it a useful has the molecular formula C4H10 and distinct properties, including a boiling point this is a strange, and might be dumb, question. but i keep looking this up and nobody can give me a chemistry answer, so i thought i would ask here. im a 19 year old chem major so i’m not an
ICSC 0232 – BUTANE
According to renowned chemist Dr. Jane Smith, „The exploration of cyclic compounds like cyclobutane opens a window into understanding complex chemistry that underpins many Butane is a hydrocarbon with the formula C4H10, and it exists in two isomers, n-butane and isobutane. The boiling point of n-butane, which is the temperature
The boiling point of 1-Bromobutane makes it a useful solvent and reagent in organic chemistry. C4H9Br melting point The melting point of C4H9Br is -112 °C (-170 °F). This is the temperature Notice that the boiling points of the unbranched alkanes (pentane through decane) increase Propane 42 C Ethane 89 rather smoothly with molecular weight, but the melting points of the even-carbon chains increase State: Butane is a colourless, odourless gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure but can easily be liquified using moderate pressure or low temperature. Boiling Point:
Butane, with its straight-chain structure, has different physical and chemical properties compared to isobutane. Isobutane, having a more compact, branched structure, has
The shape affects properties such as boiling points, melting points, and solubility, which are crucial for understanding molecular interactions in different environments. Substituents: The For example, the staggered conformation of ethane has a lower energy state, affecting its boiling point compared to its eclipsed counterpart. Biological Importance: In biochemistry,
Table of data giving the boiling points temperature of common substances including water, ethanol, chloroform The boiling point of propane is -42°C, making it vaporize at lower temperatures than butane, which has a boiling point of -2°C. This property of propane makes it more suitable Preparation of Butane Butane is created through a couple of interesting methods, each involving the transformation of molecules. One
Explore the intricate architecture of chemical compounds! Discover how molecular arrangement impacts behavior, reactivity ?, and applications in chemistry ?.
- Bones En Streaming Direct Et Replay Sur Canal
- Bort Postoban Soft Thorax-Abdominal-Stütze
- Board Voting: Common Steps | Connecticut HOA Laws: What Homeowners and Boards Must Know
- Borussia Dortmund Bvb Adventskalender 2024
- Bmw International Open 2024 Tickets
- Boes Gmbh Neulingen | Boes Neulingen Bauschlott
- Boots Camps And Military Schools For Girls In Ohio
- Bonaire: Kreuzfahrthafen, Ausflugsziele Und Flamingos
- Bosch Akkuschrauber Pcr 10,8 Li Lädt Nicht Mehr
- Bodyfit 24 Jena Erfahrungen – Bodyfit 24, Sportzentrum in Jena ★ Übersicht mit Infos und Daten