Capsaicin And Its Role In Chronic Diseases
Di: Henry
Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin sensitization is associated with declined capsaicin cough sensitivity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Yoshihiro Kanemitsu1 , Kensuke Fukumitsu1, Ryota 5 Role of Anethole in Chronic Diseases The animal and cell-line data suggest that anethole may have beneficial effects in many chronic diseases linked with inflammation, such as inflammatory conditions, cancer, diabetes, neurological diseases, since it targets many of the key players in the inflammation to cancer sequence or in the
Evodiamine and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
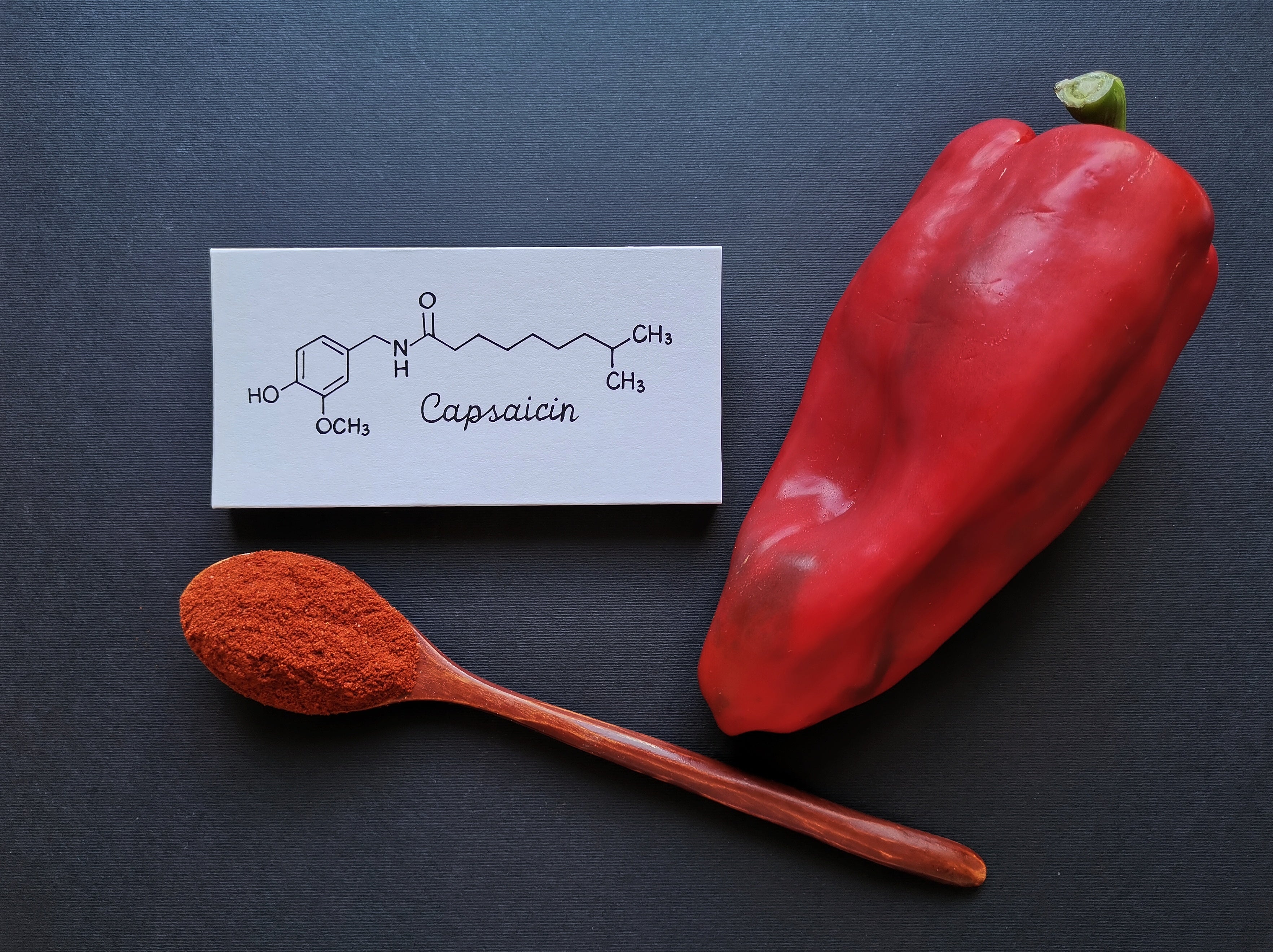
Capsaicin (8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) is one of the most important natural products in the genus Capsicum. Due to its numerous biological effects, there has been extensive and increasing research interest in capsaicin, resulting in 科研通『学术中心』是文献索引库,收集文献的基本信息(如标题、摘要、期刊、作者、被引量等),不提供下载功能。如需下载文献全文,请通过文献求助获取。 上个求助 该求助已完结,感谢关注 如需该文献,请重新发布求助, 前往发布 站在巨人的肩膀上,才更有可能跳的更远 请遵守相关知识 On the other hand, the observed experimental benefits in preventing acute kidney injury, slowing down the progression of diabetic and chronic kidney disease, ameliorating hypertension, and even
Abstract Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma are chronic respiratory diseases with high prevalence and mortality that significantly alter the quality of life in affected patients. Bioactive components obtained from plants have been used for the prevention, treatment and reduction of diseases’ symptoms. Capsaicin is the most frequently used capsaicinoids. It is the important bioactive component found in the Capsicum species. Capsaicin has an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative metabolic effects thus it is related to Abstract Capsaicin is a widespread spice known for its analgesic qualities. Although a comprehensive body of evidence suggests pleiotropic benefits of capsaicin, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-proliferative, metabolic, or cardioprotective effects, it is frequently avoided due to reported digestive side-effects. As the gut bacterial profile is strongly linked to
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma are chronic respiratory diseases with high prevalence and mortality that significantly alter the quality of life in affected patients. While
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma are chronic respiratory diseases with high prevalence and mortality that significantly alter the quality of life in affected patients. While the cellular and molecular mechanisms engaged in the Sensitization to Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) enterotoxins (SEs) A (SEA) and B (SEB) is associated with the pathogenesis of several chronic airway diseases, including asthma and chronic rhinosinusitis, but its role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) remains unclear. This cohort study aimed to investigate the impact of sensitization to SEs on
Capsaicin is a widespread spice known for its analgesic qualities. Although a comprehensive body of evidence suggests pleiotropic benefits of capsaicin, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-proliferative, metabolic, or cardioprotective effects, it is frequently avoided due to reported digestive side-effects. As the gut bacterial profile is strongly linked to
Anethole and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
Members of the genus Capsicum (Family: Solanaceae), which belongs to a dicotyledonous group of flowering plants, show fluctuating degrees of spiciness that mirror the relative concentrations of capsaicin, dihydrocapsaicin, and other analogs (nordihydrocapsaicin, homocapsaicin, and homodihydrocapsaicin) collectively known as capsaicinoids present in the Chronic disease is defined by the World Health Organization as a generally slow-progressing disease of long duration. EVO plays positive roles in curing some chronic diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases [39], by intervening on the risk factors and underlying determinants linked with chronic diseases.
Several studies have shown the neuroprotective role of capsaicin against oxidative damage, behavioral impairment, with 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induced Parkinson’s disease, pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures, global cerebral ischemia, and streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s disease. PDF | On Aug 1, 2018, George F. Antonious published Capsaicinoids and Vitamins in Hot Pepper and Their Role in Disease Therapy | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
- Capsaicin and Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease
- Anethole and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
- TRPV1 Receptor: Mechanisms, Activation, and Pain Perception
- TRPV1-Targeted Drugs in Development for Human Pain Conditions
- Mechanisms and clinical uses of capsaicin
This process known as defunctionalisation has been exploited for therapeutic use of capsaicin in various painful conditions. the less highlighted aspect in We reviewed different studies on mechanisms of action of capsaicin and its utility in different clinical conditions.
The present chapter discusses the basic mechanisms behind these two diseases and further details on the role of capsaicin in their amelioration. In addition, certain limitations related to the therapeutic uses of CAP have been discussed.
Capsaicin is a widespread spice known for its analgesic qualities. Although a comprehensive body of evidence suggests pleiotropic benefits of capsaicin, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-proliferative, metabolic, Key components in functional foods offer health benefits. Omega-3 fatty acids scavenge free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. Antioxidants in foods such as sesame seed oil promote cardiovascular health and have anti-inflammatory effects. Curcumin inhibits cancer by suppressing inflammatory Capsaicin, a major active compound from chili peppers, has been clearly demonstrated for its numerous beneficial roles in health. In this review, we will focus on the less highlighted aspect, in particular how dietary chili peppers and capsaicin consumption reduce body weight and its potential mechanisms of its anti-obesity effects.

In this review, we aimed to summarize the key evidence regarding the putative role of capsaicin on kidney function and pathophysiology and its possible therapeutic applications for treating some renal diseases. 2. Capsaicin—Biochemical Properties and Mechanism of Action
These studies could explain the beneficial health effects of capsaicin in obesity and other non-communicable chronic diseases. The influence of capsaicin on glucose homeostasis and obesity by modulation of the gut microbiota is summarized in Figure roles of capsaicin 4. Capsaicin is the most predominant and naturally occurring alkamide found in Capsicum fruits. Since its discovery in the 19th century, the therapeutic roles of capsaicin have been well characterized. The potential applications of capsaicin
Extensive research within the last several decades has revealed that the major risk factors for most chronic diseases are infections, obesity, alcohol, tobacco, radiation, environmental promised defining their Artigo pollutants, and diet. It is now well established that these factors induce chronic diseases through induction of inflammation. However, inflammation could be either acute or
In this review, we will focus on the beneficial role of capsaicin in GI tract, a less highlighted aspect, in particular how dietary capsaicin affects GI health, the mechanisms of actions and its preventive/therapeutic potentials to several GI diseases. The TRPV1 receptor is essential for detecting and responding to noxious stimuli, particularly heat and chemical irritants. Best known for its interaction with capsaicin, the compound responsible for chili pepper spiciness, it also plays a key role in pain signaling and inflammation. Understanding TRPV1 function provides insight into pain mechanisms and
Capsaicin, as a major active compound from chili pepper, has been established for its numerous beneficial roles in the human organism, including the treatment of pain inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis [28], and vasomotor rhinitis (Figure 1) [29]. Furthermore, capsaicin has proven naturally occurring an effective anti-cancer agent. Abstract Capsaicin is the most predominant and naturally occurring alkamide found in Capsicum fruits. Since its discovery in the 19th century, the therapeutic roles of capsaicin have been well characterized. The potential applications of
Bioactives significantly modify and maintain human health. Available data suggest that Bioactives might play a beneficial role in chronic inflammatory diseases. Although promised, defining their Artigo de periodico Capsaicin and its role in chronic diseases (2016) Authors: Fernandes, E. S. Cerqueira, A. R. A. Soares, A. G. Costa, Soraia Katia Pereira Autor Capsaicin (CAP), a prominent component of chili pepper known for its potent agonistic effects on TRPV1, has attracted significant attention for its diverse physiological effects. Nevertheless, there remains a paucity of data concerning its in vivo distribution, metabolism, pharmacodynamic properties, and influence on the metabolic profile of the brain.
An in-depth understanding of the biological function of TRPV1 and its role in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory skin diseases will allow the development of specific TRPV1 agonists or antagonists for the treatment of chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Sensitization to Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) enterotoxins (SEs) A (SEA) and B (SEB) is associated with the pathogenesis of several chronic airway diseases, including asthma and chronic
Digestive Disorders And Diagnosis paper discusses the potential of capsaicin as an agent to reduce inflammation in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. This evidence suggests that targeting TRPV1 may be beneficial for acne and other sebaceous diseases, though its presence in sebaceous glands and response to high dose capsaicin needs to be considered when using TRPV1-targeted treatments in wounds.
- Canva Größe Textfeld Ändern: Canva Größe Einstellen
- Canon Eos R8 In-Depth Review : Canon R8 Review: A Game-Changing Camera
- Carina Sofa Preisliste
- Canon 7D Vs 5D Mk 3: Which Is Better?
- Canon Original Tintenpatrone Pg560 Xl, Schwarz
- Carmatech Sar-12 Complete Paintball Sniper Rifle
- Canton Carat 770 Dc | Canton Karat Line Speakers
- Cartagena Rafael Nunez Airport Departures
- Carrera Bikes Range: Which Model Is Right For You?
- Can’T Turn In Marks Of Kil’Jaeden
- Carol Ann Kerrigan – Obituary information for Charles R. Kerrigan
- Carotis Chirurgie Reaktionstypen
- Caretaker Job Duty | Caregiver Activities, Duties and Responsibilities
- Cardboard Compactors: What You Need To Know
- Cape Canaveral Nach Key West , Florida Rundreise: Route, Tipps & Highlights für 1 Woche