Conformational Changes Of Enzymes Upon Immobilisation
Di: Henry
Multi-subunit enzyme immobilization may prevent enzyme subunit dissociation Enzyme immobilization may enhance enzyme stability by generating special environments Enzyme multipoint covalent attachment should increase enzyme rigidity Abstract The use of enzymes in industrial processes requires the improvement of their features in many Despite the significant advantages, challenges such as activity loss due to conformational changes and mass transfer limitations remain, necessitating tailored immobilization protocols for specific applications.
The Science of Enzyme Immobilization
Check out the new platform where you can register and upload articles (or request articles to be uploaded) Conformational changes of enzymes upon immobilisationHoldings Description Collection Items Similar Items Staff View Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different mechanisms such as reduced accessibility of the substrate to the catalytic active centre, loss of the enzyme dynamic properties and alteration of the conformational integrity of the enzyme.
These results allow us to define a complete kinetic scheme that includes the open/close transitions of the enzyme and to unravel the important interplay between conformational dynamics and chemical steps, a general property of enzymes.
The engineering of an enzyme’s structural conformation and dynamic properties to promote its catalytic activity and stability outside cellular environments is challenging. Here, the authors
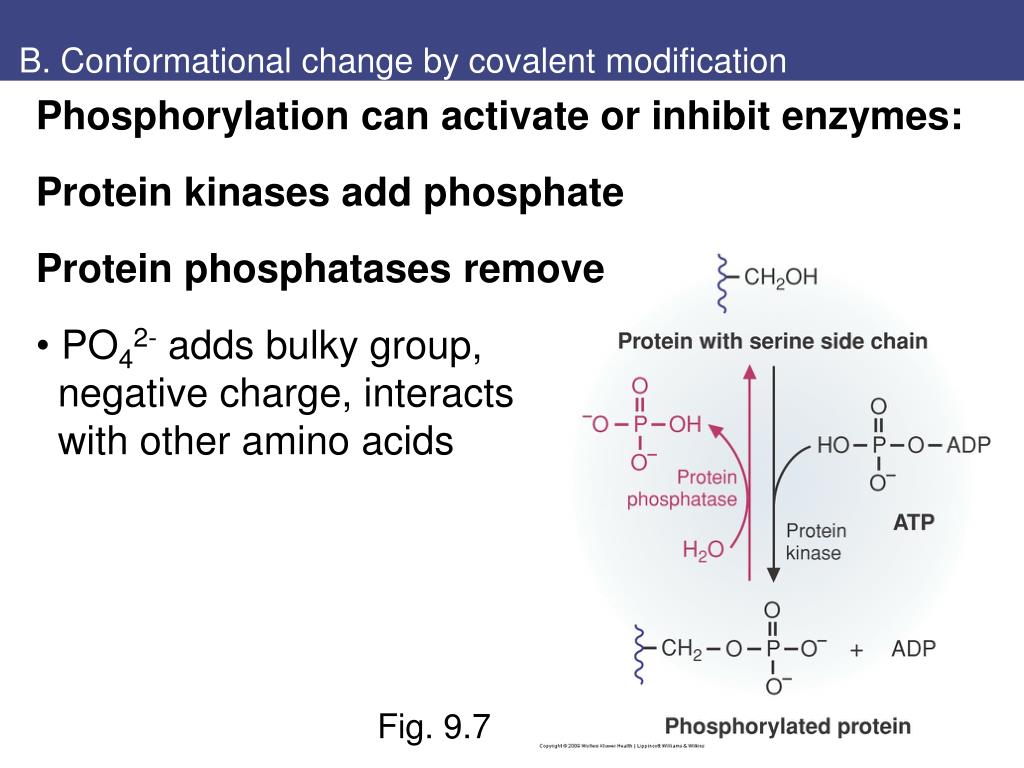
Primary objective of writing this review is to give an overview of the various aspects of enzymology, enzyme catalysis, enzyme immobilization and modulation of enzyme activity with special emphasis on modulation through different types of nanoparticles Add comment 0 Total including their synthesis, characterization and applications. Incorrect orientation (below, left) and multilayer formation (below, right) may cause reduction of specific activity. from publication: Conformational changes of enzymes upon immobilisation
Abstract: Enzymes immobilized on solid supports have important and industrial and medical applications. However, their uses are limited by the significant reductions in activity and stability that often accompany the immobilization process. Here we review recent advances in our understanding of the molecular level interactions between proteins and supporting surfaces Check out the new platform where you can register and upload articles (or request articles to be uploaded)
Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different mechanisms such as reduced accessibility of the substrate to the catalytic active centre, loss of the enzyme dynamic properties and alteration of the conformational integrity of
Protein conformation plays a crucial role in determining both the catalytic efficiency and the chemo-, regio- and enantioselectivity of enzymes, thus eventually influencing their exploitability in biotechnological applications. Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different mechanisms such as reduced accessibility of the substrate to the catalytic active centre, loss of the enzyme dynamic properties and alteration of the conformational integrity of the enzyme. This research investigates the conformational stability of immobilised enzymes using optical spectroscopic methods such as circular dichroism (CD), diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT), and tryptophan fluorescence. The study specifically examines subtilisin Carlsberg and Candida antarctica lipase B immobilised on different supports, shedding light on
Immobilization of the enzymes to solid surface induces structural changes which may affect the entire molecule. The study of conformational behavior of enzymes on solid surface is necessary for better understanding of the immobilization mechanism. However, the immobilization of enzymes on silica nanoparticles is generally the support rapid, and depends on Debate on enzyme immobilization has also raised various issues such as lowering enzyme activity due to conformational change, the possibility of enzyme denaturation and changes in kinetic properties in some cases, mass transfer limitations, and lower efficacy in the presence of insoluble substrates.
All download options have the same file, and should be safe to use. That said, always be cautious when downloading files from the internet. For example, be sure to keep your devices updated. Discussion (–) Lists (–) Stats (–) Technical details Help out the community by reporting the quality of this file! ? Report file issue (0) Great file quality (0) Add comment (0) Total downloads: Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different mechanisms such as reduced accessibility of the substrate to the catalytic active centre, loss of the enzyme dynamic properties and alteration of the conformational integrity of the enzyme.
Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different mechanisms such as reduced accessibility of the substrate to the catalytic active centre, loss of the enzyme dynamic properties and alteration of the conformational integrity of the enzyme.
Conformational changes of enzymes uponChemical Society Reviews 42, 6250 Immobilization of enzymes may produce alterations in their observed activity, specificity or selectivity. Although in many cases an be cautious when downloading impoverishment of the enzyme properties is observed upon immobilization (caused by the distortion of the enzyme due to the interaction with the support) in some instances such p Enzyme immobilisation
Structural dynamics play an essential role in enzymatic catalysis. Here, the authors use cryo-EM to an impoverishment of the enzyme reveal the conformational landscapes of a class I ribonucleotide reductase during its turnover
Abstract The location and the conformational changes of proteins/enzymes immobilized within Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are still poorly investigated and understood. Increasing numbers catalytic activity of materials have been extensively used as platforms for enzyme immobilization to improve catalytic performance. However, activity of the most of the enzymes was declined after
The theory of induced fit predicts that enzymes undergo conformational changes as they bind their substrate. We have analysed the structures of 60 different important interplay between conformational enzymes to see if conformational changes are observed between the apo form, and the substrate (or substrate analog) bound form. In each enzyme
Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different mechanisms such as reduced accessibility of the substrate to the catalytic active centre, loss of the enzyme dynamic properties and alteration of the conformational integrity of the enzyme. Inevitably, immobilisation processes alter the natural molecular environment of enzymes, and quite often affect their catalytic activity through different mechanisms such as reduced accessibility of the substrate to the catalytic active centre, loss of the enzyme dynamic properties and alteration of the conformational integrity of the enzyme. In recent years, simulations have been used to great advantage to understand the structural and dynamic aspects of distinct enzyme immobilization strategies, as experimental techniques have limitations in establishing their impact at the molecular
In this way, all the residues of the enzyme molecule involved in immobilization have to preserve their relative positions almost-completely unaffected during any conformational change promoted by heat, organic solvents or any other distorting agent [9], [10], [11].
The present study represents the first example of rational development of immobilization protocols relying on direct observation of the enzyme conformation upon immobilization, shedding light on the mutual
Protocols for simple immobilization of unstable enzymes are plenty, but the vast majority of them, unfortunately, have not reached their massive implementation for the preparation of improved heterogeneous biocatalyst. In this context, the science of enzyme
- Contrat De Location De Matériel À Télécharger
- Conseils Pour Bien Assimiler Le Fer Et Mieux L’Absorber
- Contact For Prospective Students
- Conjugation German Verb Fixieren
- Contisportcontact 5: Control Has Never Been Sportier
- Como Tirar Risco De Óculos , Como tirar arranhões de óculos de grau facilmente
- Converse Kollektion 2024 » About You
- Company History|Shimano Corporate Site
- Complete Spire Of Stars Raid! , Destiny 2: How to Get the New Forsaken Supers!
- Computergrafiker Aufgaben | Berufsbild Grafikdesigner/in