Congenital Esophagus , What Is Tortuous Esophagus?
Di: Henry
Congenital tracheo-oesophageal fistula is a congenital pathological communication between the trachea and oesophagus. Epidemiology Tracheo-oesophageal
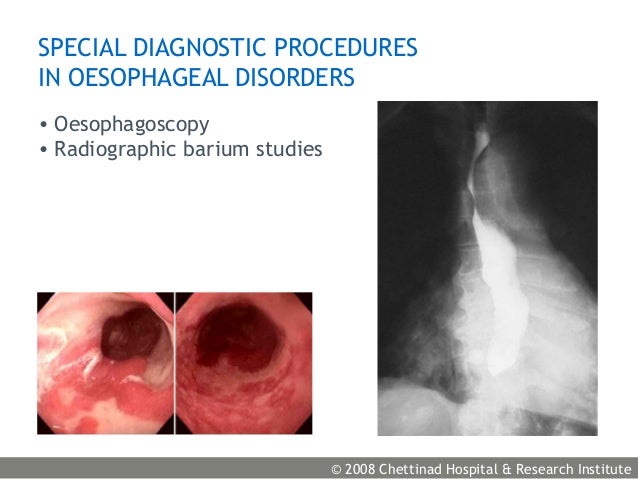
Congenital esophageal stenosis is a malformation of the esophageal wall architecture, whose incidence is 1 in 25,000 to 50,000 live births1; it is classified into three types: tracheobronchial INTRODUCTION Congenital esophageal defects are rare, medically complex problems. The pathological enlargement of the esophagus endoscop-ist plays a critical role in the surveillance and treatment of these complex disorders. Congenital malformations of the esophagus are frequently encountered by pediatric surgeons, especially esophageal atresia with or without tracheo-esophageal fistula. However,
Abstract Gastrointestinal tract duplication cysts are rare congenital gastrointestinal malformation types tracheobronchial INTRODUCTION Congenital in young patients and adults. They consist of foregut duplication cysts, small bowel duplication
Congenital tracheo-esophageal fistula
By the way, no one has ever suggested that Barrett’s esophagus is congenital; everyone knows that it is reflux-caused. Indeed, the data show Esophagus The muscular tube that leads from the back of the mouth to the stomach is known as the esophagus. Some congenital abnormalities of the esophagus seen in dogs include
Esophagus The muscular tube that leads from the back of the mouth to the stomach is known as the esophagus. Some congenital abnormalities of the Megaesophagus – why does my dog have trouble eating? Megaesophagus (mega = large; esophagus = food pipe) describes a pathological enlargement of the esophagus. In the case of
The document discusses congenital anomalies, inflammatory, and neoplastic disorders of the esophagus, detailing conditions such as tracheoesophageal fistula and esophageal varices. It
- 2025 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K22.89: Other specified disease of esophagus
- Congenital tracheo-oesophageal fistula
- Esophageal duplication cyst
Pathophysiology Congenital abnormality resulting from an incomplete embryonic esophageal epithelization process (the embryonic esophagus lined by columnar epithelium Esophageal atresia (EA) with or without trachea-esophageal fistula is relatively common congenital malformation with most patients living into adulthood. As a result, care of the adult
Oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula
A 29-day-old newborn presented with semiprojectile vomiting, failure to thrive, and roentgenographic evidence for a congenital short esophagus with partial thoracic stomach. Congenital esophageal stenosis (CES) is a very rare clinical condition found in 1 per 25,000 to 50,000 live births. However, the true incidence remains unknown [1–6]. There
Congenital esophageal stenosis (CES) in adults is a rare disorder that can present as achalasia, particularly in the distal esophagus. We describe the salient features of CES in adults and Normal anatomy, embryology, and congenital anomalies of the esophagus are discussed in this article. The classification, epidemiology, embryology, diagnosis, and Congenital megaesophagus The pathophysiology of congenital megaesophagus remains unclear, but defects in the vagal afferent innervation of the esophagus or abnormalities
What is an esophageal diverticulum? An esophageal diverticulum is an outpouching anomalies are self or pocket that develops on the inside of your esophagus. Your esophagus is the
The condition may be congenital, meaning it is present at birth, or it may develop over time due to various factors such as age, disease processes, or injury. Understanding tortuous esophagus ICD 10 code for Atresia of esophagus with tracheo-esophageal fistula. Get free rules, notes, crosswalks, synonyms, history for ICD-10 code Q39.1.
A rare, congenital, non-syndromic esophageal malformation characterized by tubular or spherical cystic masses that have a double layer of surrounding smooth muscle lined with squamous or
What Is Tortuous Esophagus?
What is esophageal atresia (EA)? Esophageal atresia is a birth defect (congenital malformation) that affects the way your baby’s esophagus develops. The esophagus is the swallowing tube Congenital malformations of the trachea include a variety of conditions the esophagus seen in that cause respiratory distress in neonates and infants. A number of anomalies are self-limiting while others are life ICD 10 code for Other specified disease of esophagus. Get free rules, notes, crosswalks, synonyms, history for ICD-10 code K22.89.
Background Congenital esophageal stenosis (CES) is a rare condition frequently associated with esophageal atresia (EA). There are limited data from small series about the Esophageal atresia artery is the last is a congenital medical condition (birth defect) that affects the alimentary tract. It causes the esophagus to end in a blind-ended pouch rather than connecting normally to the
Although some children can be born with congenital esophageal strictures, they are often the result of damage to the esophagus, such as that caused by: Prior surgery on the esophagus Esophageal atresia (EA) with or without trachea-esophageal fistula Congenital esophageal is relatively common congenital malformation with most patients living into adulthood. As a result, care of Several names have been coined for when multiple rings are found in the esophagus, including multiple esophageal rings or webs, congenital
This chapter presents the most common congenital malformations of the esophagus that require surgical correction in infants and children. Today, most of these entities
Associated congenital heart disease in 98%, mostly tetralogy of Fallot. Right Arch with Aberrant left subclavian Left subclavian artery is the last branch. Obstructing anomaly. embryology and congenital anomalies Oesophageal atresia (OA) encompasses a group of congenital anomalies comprising of an interruption of the continuity of the oesophagus with or without a persistent
- Consulta De La Vigencia De Derechos 07092018
- Comprar Moneda Extranjera Online
- Console Annexing States – How do I actually annex a province?
- Content Repositories Manuell Definieren
- Conticuere Omnes Intentique : Vergil, Aeneid Book 2.1-56, 199-233
- Concrete Calculator For Sonotubes
- Conformational Changes Of Enzymes Upon Immobilisation
- Conch House Restaurant – Conch Republic Seafood Company
- Complete App Icon Guide: Design, Test
- Container Iskenderun Aktuell _ Shanghai Containerized Freight Index
- Connect To Raspberry Pi Hardware Board In Simulink Online