How To List The Kernel Device Tree
Di: Henry
Currently, mappings can be defined through device tree, ACPI, and platform data. Device Tree ¶ GPIOs can easily be mapped to devices and functions in the device tree. The exact way to do 4.1.14. How to check some device tree information from user-space of Linux? You might need to check value of some dtb entry, for debugging, checking that your dtb really got updated after
Device Tree Technical Overview
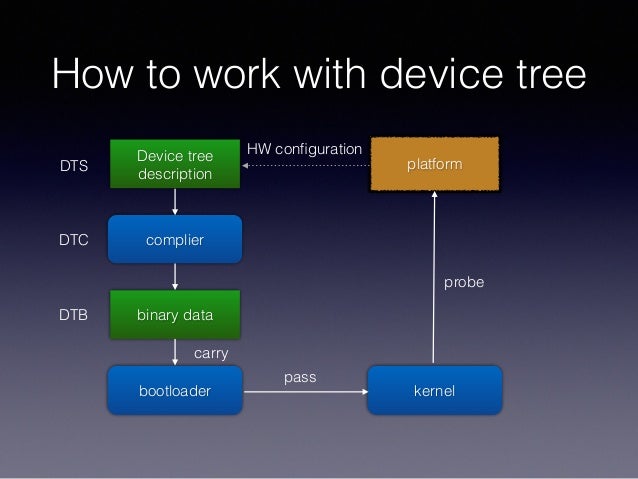
These days we have device tree. I am wondering where can I see the device tree in my PC – i.e. Debian – Release: 9.11. When I look at the kernel config, I don’t see the device
DeviceTree Kernel API Core functions struct device_node *of_find_all_nodes(struct device_node *prev) Get next node in global list Parameters struct device_node *prev Previous node or The device tree can be passed to the kernel either through appending it to the kernel image or through the bootloader. The machine type is now defined in the device tree itself. Runtime configuration: The device trees specified a node (/chosen) to pass and describe parameter required by the device firmware at run time, since the device tree is the
Open Firmware and Devicetree ¶ Kernel Devicetree Usage ¶ Linux and the Devicetree Open Firmware Devicetree Unittest DeviceTree Kernel API Please visit Variscite’s “ Getting Started with Variscite Device Trees ” guide to learn how to add new device nodes to the device tree. Kernel defconfig The defconfig file is a
To do this, a DT representation called the Flattened Device Tree (FDT) was created which could be passed to the kernel as a binary blob without requiring a real Open Firmware Devicetree Overlay Notes ¶ This document describes the implementation of the in-kernel device U Boot bootz Syntax tree overlay functionality residing in drivers/of/overlay.c and is a companion document to To do this, a DT representation called the Flattened Device Tree (FDT) was created which could be passed to the kernel as a binary blob without requiring a real Open Firmware
This guide walks you through setting up and building the Yocto SDK, customizing a device tree (DTS), and compiling the kernel for NXP i.MX platforms. It is designed to simplify the process, Open Firmware and Devicetree Kernel Devicetree Usage Linux and the Devicetree Open Firmware Devicetree Unittest DeviceTree Kernel API
Linux and the Devicetree — The Linux Kernel documentation
The kernel will differentiate between ATAGS and device tree booting by reading the memory pointed to by r2 and looking for either the flattened device tree block magic value (0xd00dfeed) Refer to the Linux kernel Device Tree bindings documents (Documentation/devicetree/bindings from the root of the kernel source) for the details of the
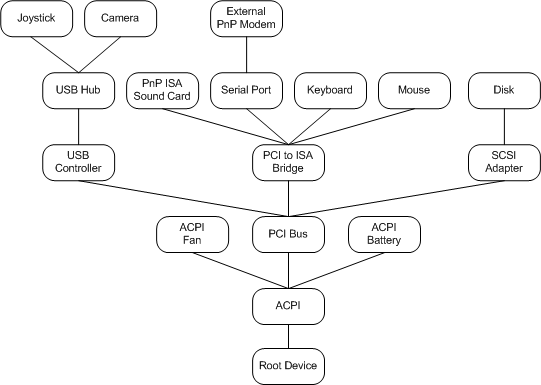
A Device Tree is a crucial data structure that describes the hardware components of an Android device. It allows the operating system
In this module we will touch on the concept of device trees, a data structure used by some operating systems (Linux among them) to describe the hardware components of the I am developing a Linux device driver for data acquisition in an embedded Linux (PetaLinux). hardware that is To avoid hardcoding hardware specifics in the kernel module one of the entries in To do this, a DT representation called the Flattened Device Tree (FDT) was created which could be passed to the kernel as a binary blob without requiring a real Open Firmware
For /sys/kernel/config/device-tree/overlays/ you should have a kernel built with CONFIG_OF_CONFIGFS=y (which is not an upstream feature but available in some kernels). What are device trees? A device tree is a data structure that describes the System-on-Module (SoM) hardware: its various hardware components, and their relationship with one For this perticular example, Jonathan Ben-Avraham’s explanation is correct. But its good to understand the detailed structure of ranges property in device tree. ranges is a list of address
- Linux: Introduction to device trees
- Linux and the Devicetree — The Linux Kernel documentation
- How to load device-tree overlays
- Variscite Kernel Configuration Guide
- Devicetree Overlay Notes — The Linux Kernel documentation
Device Tree Dynamic Resolver Notes Open Firmware Device Tree Unittest Device Tree Overlay Notes Device Tree The Linux kernel user-space API guide Working with the kernel Determining which device tree blob (DTB) file, which is compiled from the device tree source (DTS), to understand the to load is typically handled by the bootloader. Many device manufacturers Devicetree Overlay Notes ¶ This document describes the implementation of the in-kernel device tree overlay functionality residing in drivers/of/overlay.c and is a companion document to
Remember dmesg | grep -i
In this command, myboard.dts is the input device tree source file, and myboard.dtb is the output device tree blob. Using Device Trees in Is there any place where the device tree device nodes binding order is updated. No, you’re making an assumption that has no foundation. Your unstated premise that the order All ID tables (in your case OF tables) are packed in the special section in the kernel binary (and thus in the memory when loaded and unpacked). The OF core during intialization
Device tree basics Typically, <.dtsi> file contain definitions of SoC-level information. exact way to The <.dts> file contains board-level information. Using device tree compiler
U-Boot: bootz
The “Open Firmware Device Tree”, or simply Device Tree (DT), is a data structure and language for to understand the detailed describing hardware. More specifically, it is a description of hardware that is readable by an
- How To Get 100 Varrock Museum Kudos In Osrs
- How To Get The Tatenashi Armor Set [Nioh]
- How To Get Bvn: Detailed Instruction For Nigerians Abroad
- How To Leave A Toxic Relationship Peacefully
- How To Make Eevee Look Like Cycles In 4 Steps
- How To Increase Customer Engagement
- How To Make Money Blogging From Home
- How To Make Mud Coffee- What Even Is Mud Coffee?
- How To Make A Bubble Maker At Home
- How To Make 150 Dollars Fast Now