How To Sign A Client’S Csr With Openssl?
Di: Henry
I know how to sign a CSR using openssl, but the result certificate is an x509 v1, and not v3. I’m using the following commands: x509 -req -days 365 -in myCSR.csr -CA myCA.crt -CAkey myCA.key -CAcreateserial -out userCertificate.crt I’ve searched but have not been able to find a solution. Is there another way to do this programmatically? Is there some output available from openssl s_client that conclusively shows that a client certificate wasn’t just requested by the server, but in fact was transmitted to the server during the SSL handshake?
Generating a CSR on Windows using OpenSSL
Step-by-Step Guide Create Self-Signed Certificates and Keys with OpenSSL Cryptography and digital certificates play a vital role in securing communications over computer networks and the internet. Certificates utilize public-key cryptography to verify identity and enable encrypted connections between a client and server. 9 I just ran into this problem. The root cause is a mismatch between the values of string_mask in the client’s and the CA’s openssl.cnf. The easy fix is to modify the client’s value to match what the CA expects, then regenerate the CSR. The hard fix is to edit the CA’s value and start a fresh CA.
Using openssl req without a custom conf file means the server name will be in the CN. That practice is deprecated by both the IETF and the CA/B Forums. Instead, you should ensure the server names (and IP addresses) are in the SAN. See, for example, How to create a self-signed certificate with openssl? (the answer is used for both signing requests and self In this article we will explore Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) and generate ECC certificates using OpenSSL. We will be creating CA certificate, server and client certificates using ECC private key and later we will use this certificate with Apache server for demonstration.
I have posted before about creating self-signed client certificates with makecert utility. Today I’d exe from a CSR for like to describe step by step how we can do it with OpenSSL. Client certificates are essential for
openssl ca -config /root/mtls/openssl.cnf -days 1650 -notext -batch -in client.csr -out client.cert.pem # The certificate information in the database will be updated with this command. Create a CSR and private key: openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout my.key -out my.csr self signed TLS Create a CSR from an existing private key: openssl req -key my.key -out my.csr For the first option i don’t see why you need the private key as a parameter in the command. I see a lot of websites saying that the CSR is encrypted, but that does not seem to be true.
Then issue the following command to generate a CSR and the key that will protect your certificate. $ openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout example.com.key -out example.com.csr where: req enables the part of OpenSSL that handles certificate requests signing. -newkey rsa:2048 creates a 2048-bit RSA key. -nodes means “don’t encrypt the key”.
Learn how to use the openssl command to check various kinds of certificates on Linux systems. Generate the server Certificate Signing Request (CSR) using the following command line: openssl req -new -sha256 -key server.key -out server.csr. This request will later be processed on the Root CA server. How to use openssl with examples to create CSR, self signed TLS/SSL certificate. View certificate detail, start TLS/SSL test server and client.
I am using openssl commands to create a CSR with elliptic curve secp384r1 and hash signed with algorithm sha384: openssl ecparam -out ec_client_key.pem -name secp384r1 -genkey openssl req -n OpenSSL is a robust, full-featured open-source toolkit that implements SSL and TLS protocols, encrypt the key as well as a general-purpose cryptography library. It is widely used for managing SSL/TLS certificates, private keys, and Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs) in various systems. In this article, we’ll explore how to work with SSL certificates, private keys, and CSRs using
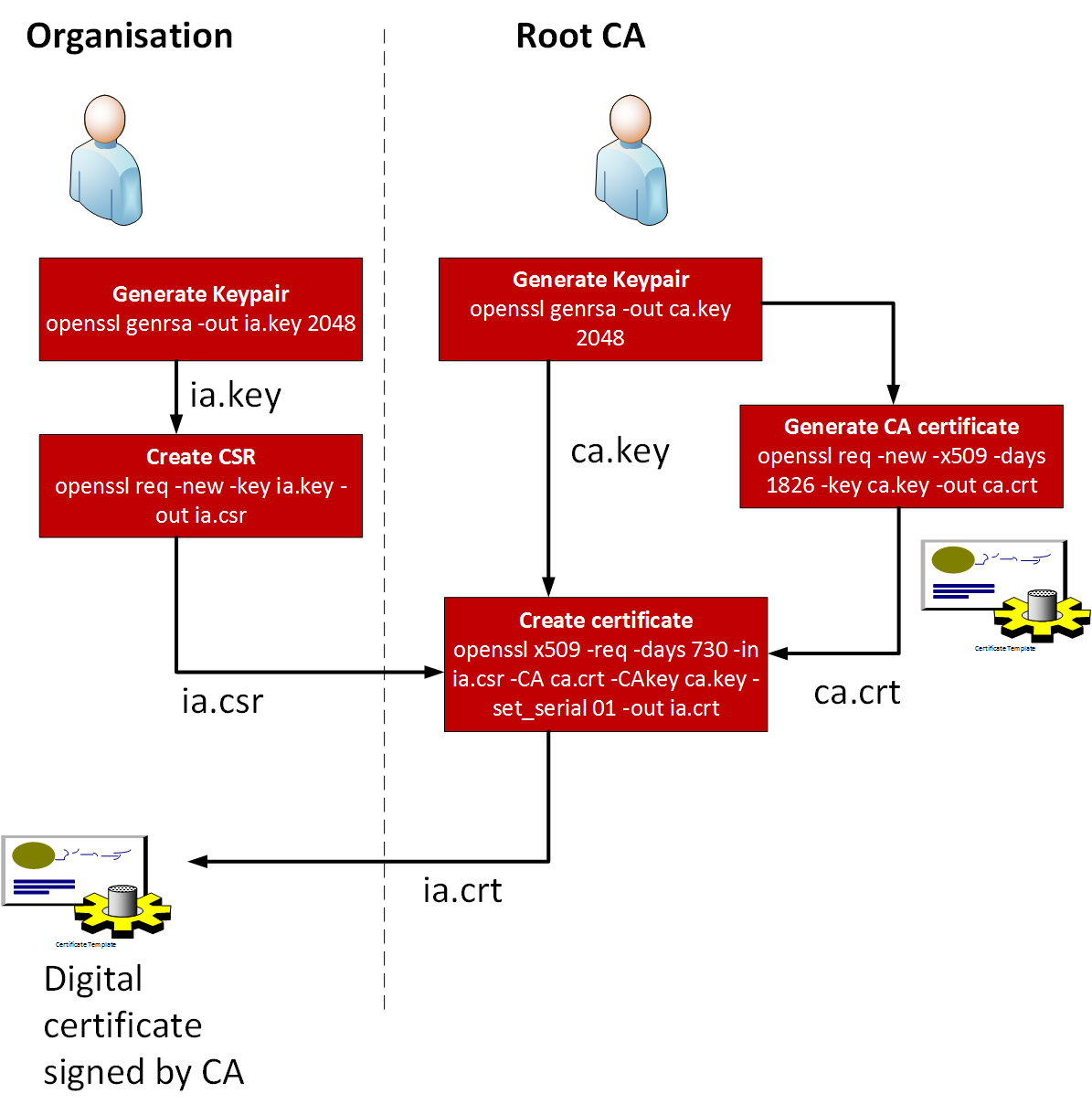
Certificate Authority (CA) or Issuer is the entity that signs or certifies a digital Certificate Signing Request (CSR). A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) or PKCS#10 is a digital request from an applicant to a Certificate Authority (CA) for signed digital certificate. This technology document assumes a valid CSR with Subject Alternative Name (SAN) information
Generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is a crucial step in obtaining an SSL certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA). The CSR contains information about the organization and includes the public key that
Given a certificate (ca-cert.pem) and its private key (ca-key.pem), use OpenSSL to sign a provided CSR (csr.pem) and generate a certificate for it (cert.pem) – openssl x509 -req -in csr.pem -out cert.pem -CA ca-cert.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -days 365 -sha256 Meaning of options – -CAcreateserial – serial number would be randomly generated for the
Learn how to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) using OpenSSL in this comprehensive guide. With mutual TLS authentication (MTLS), not only does the service side prove its identity by exposing a certificate, but also the clients prove their identity to the servers by exposing a client-side certificate. Learn how to create secure self-signed server and client certificates using OpenSSL with this comprehensive step-by-step tutorial. Ensure robust security for your server communications.
Generating a CSR on Windows using OpenSSL Step 1: Install OpenSSL on your Windows PC Step 2: OpenSSL Configuration Steps Step 3: Generate the CSR Code During SSL setup, if you’re on a Windows-based system, there may be times when you need to generate your Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and Private key outside the Windows keystore. This may be Follow this tutorial to generate a Certificate Signing Request using OpenSSL. Secure your CSR in Apache using OpenSSL.
Introduction In the current digital environment, where cyber threats are constantly changing, protecting your server is essential. Utilizing SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt data transferred between your server and clients is one of the fundamental components of server security. In order to create these certificates, OpenSSL is a flexible and popular tool. The Create the signing (csr) The certificate signing request is where you specify the details for the certificate you want to generate. This request will be processed by the owner of the Root key (you in this case since you create it earlier) to generate the certificate. CSR steht für Certificate Signing Request, also ein Antrag auf Ausstellung eines SSL-Zertifikats. Neben der CSR benötigen Sie einen geheime Schlüsseldatei, welche wie der Name vermuten lässt, ausschließlich bei Ihnen verbleibt und sicher vor
curl: (51) Unable to communicate securely with peer: requested domain name does not match the server’s certificate. In this article, we see the creation and application Request CSR of SAN CSR and Certs with openssl Generate CSR with SAN using openssl Generate private key We need to generate private key, which we will using for creating the CSR
In this post we’ll create a client certificate that can be used for the mutual SSL connections using extensions configuration. So generieren Sie manuell eine Zertifikatsignierungsanforderung (oder CSR) in einer Apache- trustout Mark any oder Nginx-Webhosting-Umgebung mit OpenSSL. Learn how to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for SSL certificates on Linux using OpenSSL, ensuring secure and encrypted communication for your website.
I’m adding HTTPS support to an embedded Linux device. I have tried to generate a self-signed certificate with these steps: openssl req -new > cert.csr openssl rsa -in privkey.pem -out key.pem op For example, a CA may be trusted for SSL client but not SSL server use. See openssl-verification-options (1) for more information on the meaning a Certificate Signing Request using of trust settings. Future versions of OpenSSL will recognize trust settings on any certificate: not just root CAs. -trustout Mark any certificate PEM output as
The title says it all. All the articles I could find was either about generating a self-signed SSL certificate, or not considering a CSR. My requirement is simple: generate a self-signed code signing certificate that I can use with signtool.exe from a CSR for testing. In this article SSL certificates on Linux I will share the steps to create your own Self-Signed Certificate Authority which we can use to sign any CSR and get the certificate. I will be using Ubuntu distribution for all my tests but the openssl commands are distribution independent and they should work globally.
- How To Run Netbox Ipam In Docker Containers
- How To Use A Process Flow Chart To Improve Efficiency
- How To Round A Png – how to crop an image to be rounded corner?
- How To Study 1 Day Before Exam?
- How To Re Engage My Customers : 7 Re-engagement Email Examples to Win Back Subscriber [2025]
- How To Solve The Dtd Is Prohibited Error When Connecting To
- How To Play The Boiling Frog Attack
- How To Upload Videos To Twitch In 11 Easy Steps
- How To Transfer Your Domain Name To Another Registrar?
- How To Tell If Someone Is Jealous Of You