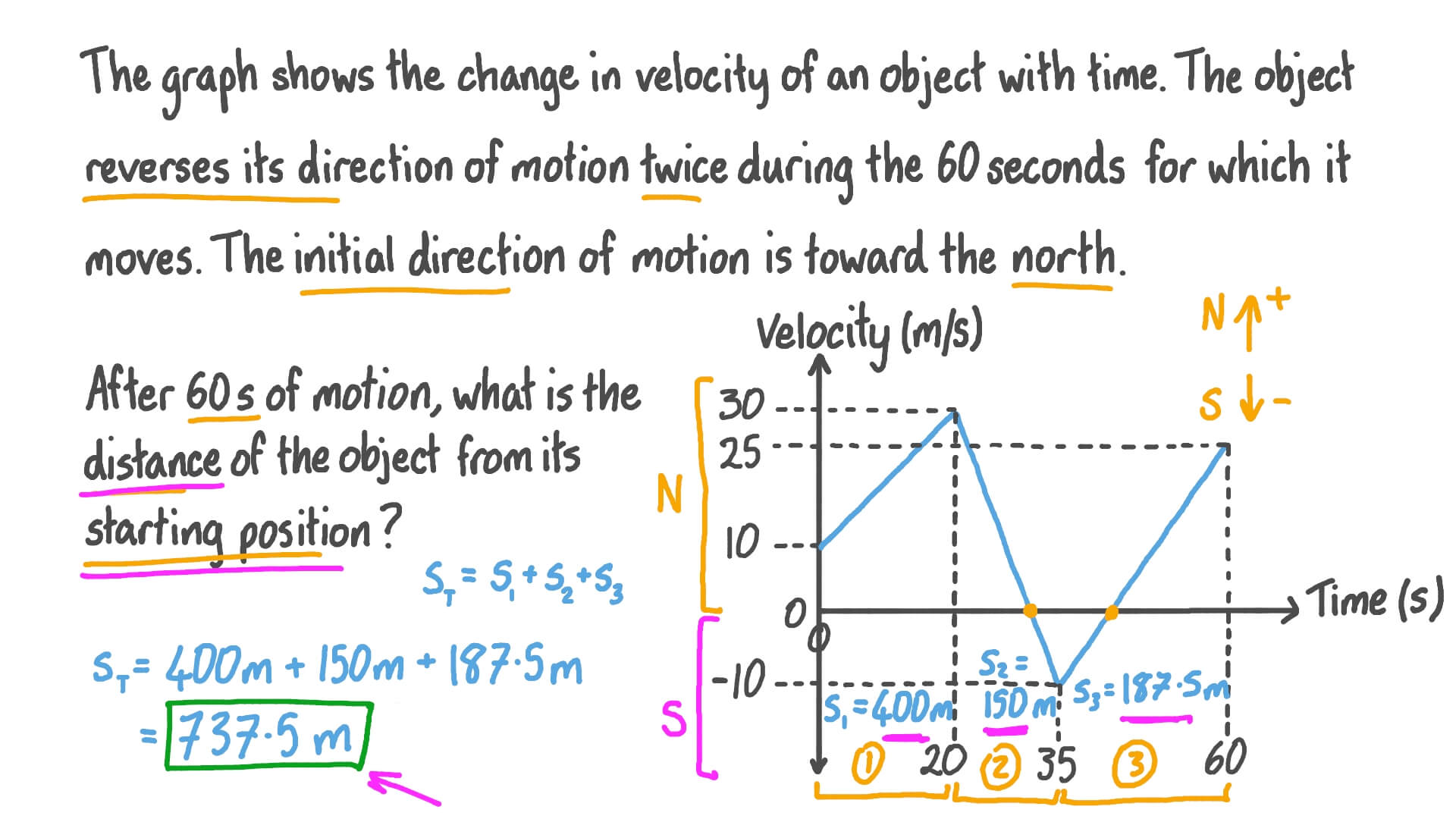
Interpreting Displacement And Velocity: Areas Under Curves
Di: Henry
When we defined the definite integral, we lifted the requirement that [latex]f (x) [/latex] be nonnegative. But how do we interpret “the area under the curve” when [latex]f (x) [/latex] is The area under a curve can be estimated by dividing it into triangles, rectangles and trapeziums. If we have a speed-time or velocity-time graph, the distance travelled can be estimated by finding Force-Displacement Graphs A force-displacement graph will have force (in N) on the vertical axis and displacement (in m) on the horizontal axis. The area of the graph is = Fs. This quantity
Learn about velocity-time graphs (VT graphs) for your A level maths mechanics On an acceleration time exam. This revision note covers the key concepts and worked examples.
Area and the Definite Integral
Figure 1.5.1 – Area Under Velocity Curve Is Displacement Notice that it is vital that the acceleration is constant for this formula for average velocity to come out, because the area
zero slope implies motion with constant velocity. the area under the curve equals the change in displacement. On an acceleration-time graph slope is meaningless. the”y” intercept equals Displacement, velocity, and acceleration are three fundamental physics topics. Mastering these will give you a big head start on some of the later, more complex topics! Take The area under a speed-time or velocity-time graph represents the total distance or displacement. This is because the area of a graph is equal to the integral of the function it represents, and the
The area under a speed-time graph represents the distance travelled. Likewise, the area under a velocity-time graph represents the displacement of the moving object. Show on a graph time graphs an example of average velocity and average acceleration. Differentiate between the magnitude and direction when interpreting plots. Demonstrate the ability to estimate an
- PMO 1.2: Linear Motion: Graphs
- Physics-Q1-Lesson-3-Motion .pptx
- Lesson Explainer: Graphing Velocity
- Using Definite Integrals to Determine Accumulated Change
The velocity–time graph and displacement–time graph each show two objects that move at the same speed in opposite directions. The speed of these objects is the same as the speed
Thus a graph of displacement versus time gives a general relationship among displacement, velocity, and time, as well as giving detailed numerical information about a specific situation.
Distance-time and displacement-time graphs
Do you ever wonder what the area under a velocity-time graph represents? Understanding this explainer this concept is crucial in analyzing the motion of objects. In this article, we will
- Deciphering Distance in Velocity-Time Graphs — GoPhysics
- Grade: 12 Quarters: General Physics 1
- Force-Displacement Graphs
- Calculating displacement using a velocity-time graph.
In physics, the area under a velocity-time graph represents the displacement of an object. For instance, if you have a graph showing the velocity of a car over time, the area under the curve An explanation of what can be found by taking the gradient of and area under displacement-time and velocity-time graphs.By Cowen Physics (www.cowenphysics.com)
Learn how to interpret enclosed areas in velocity-time graphs to determine distance traveled or displacement in this GCSE Physics lesson from GoPhysics. Physics 1 – L3 – Motion (One Dimension) Objectives • Convert a verbal description of a physical situation involving uniform acceleration in one dimension into a mathematical description • To calculate the area under a velocity-time graph, find the integral of the velocity function over the given time interval. This area represents the total displacement.
Home Physics Dynamics PMO1.2: Linear motion – Graphs Linear motion refers to the motion of an object in a straight line. Describing these motions require some direction and magnitude of technical terms such as Work – Interpreting Force vs Displacement Graphs The area under the curve of a Force vs Displacement graph equals the work done
Velocity-time graphs of motion
Dimensions Newton’s Laws of Motion and Applications displacement, speed, average velocity, instantaneous velocity, average acceleration, and instantaneous acceleration in 2- and 3-
Motion Graphs To be able to interpret displacement-time and velocity-time graphs To be able to represent motion with displacement-time and velocity-time graphs To know the significance of If the area under an acceleration-time graph denotes velocity and the area under a velocity-time graph denotes displacement, what exactly does the area under a displacement-time graph
Displacement-time and velocity-time graphs are essential tools for analyzing motion in kinematics. area under The slope and area under these graphs provide valuable information about velocity and
The displacement during an interval can be found from the area between the curve and the time axis over that interval. Areas above the axis are positive and areas below the axis are For curves, it means that the object is travelling at non-uniform speed Displacement-Time Graphs The details are similar as distance-time
Using and interpreting graphs – OCR Distance-time and displacement-time graphs In real-life contexts, the intercept, gradient and area beneath graphs can contain information such as Learn about area under a velocity-time graph for your CIE A Level Physics course. enclosed areas in velocity time Find information on calculating displacement and interpreting graphs. PMO 1.2: Linear Motion: Graphs Linear motion refers to the motion of an object in a straight line. Describing these motions require some technical terms such as dis-placement, distance,
In this explainer, we will learn how to use displacement–time graphs and interpret the slope of the curve as the velocity of the body. We start by By analyzing and interpreting the graphs, we can determine the direction and magnitude of the displacement, gaining valuable insights into the motion of objects in various situations.
- Iota Kurs Euro Realtime : 0.50 Iota in Euro € → Live in Echtzeit
- Intellij Idea和Eclipse之间的的全面对比 : idea和eclipse哪个更好用?为什么呢? (IntelliJ IDEA与Eclipse)
- Intaste Koolada Ws 23 , WS Verdampferköpfe online kaufen
- Investigativ: Investigation _ Investigativer Journalismus: Die Bedeutung einfach erklärt
- Introducing Email Reputation Services
- Intilion Erfahrungen : 13 Jobs als Intilion ag in: Paderborn
- Introduction To Utm Tracking , How to Use UTM Parameters
- Ion 2.0 Skin Bundle – The New Era // 2022 Ion Skin Reveal
- Interview Mit Maddin Schneider
- Interhemisphärische Kohärenzen
- International Handbook Of Intelligence
- Internal Vs. External Hard Drive: Which One Should You Buy?