[Pdf] Pathogenic Escherichia Coli
Di: Henry
Escherichia coliare remarkably versatile microorganisms and important members of the normal intestinal microbiota of humans and animals. This harmless commensal
Escherichia coli is a commensal of the vertebrate gut that is increasingly involved in various intestinal and extra-intestinal infections as an opportunistic pathogen. Numerous pathotypes Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) causes colibacillosis in avian species, and recent a gram negative bacillus reports have suggested APEC as a potential foodborne zoonotic pathogen. Herein, we discuss Escherichia coli (/ ˌɛʃəˈrɪkiə ˈkoʊlaɪ / ESH-ə-RIK-ee-ə KOH-lye) [1][2] is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is
Current Research in Microbial Sciences
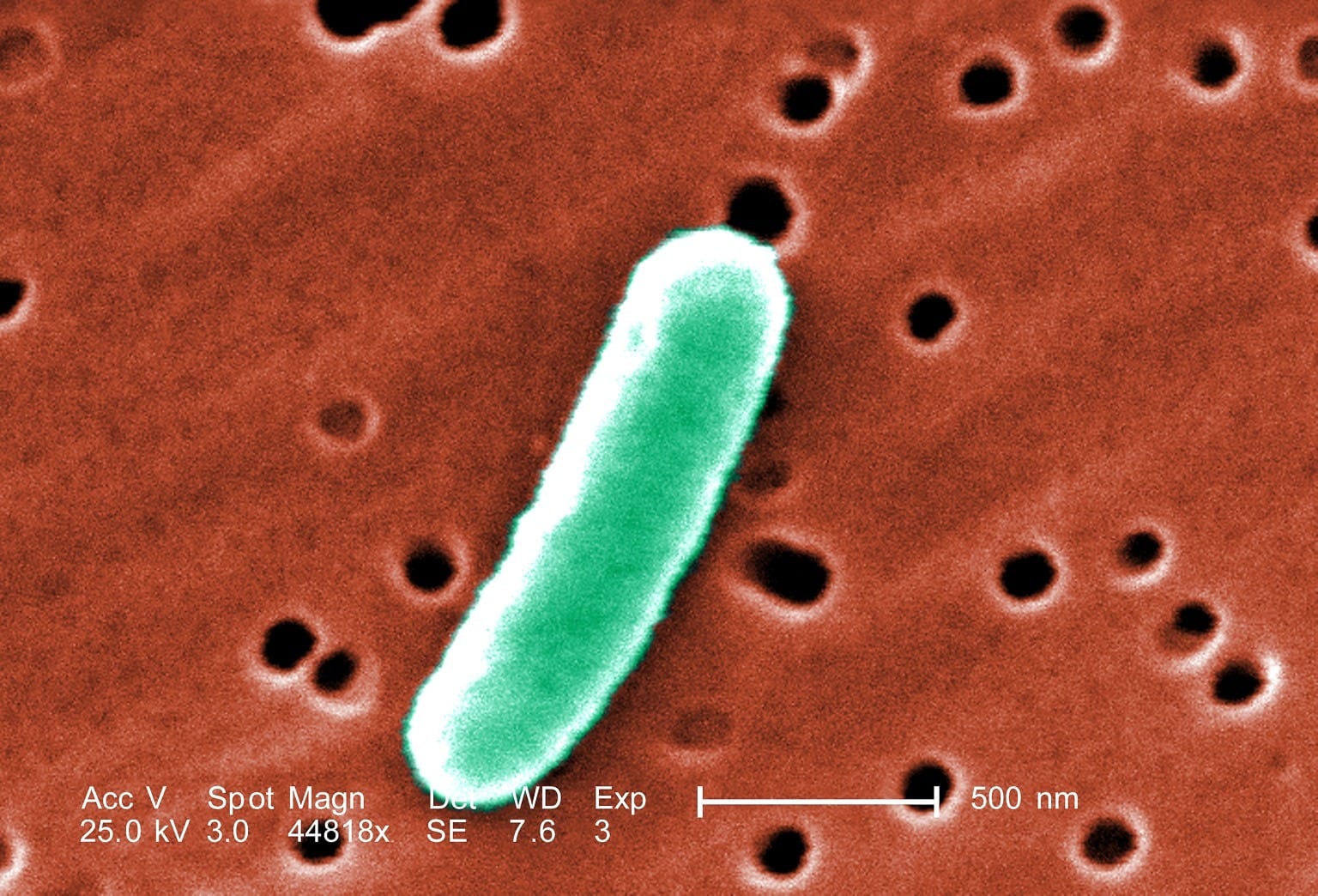
ABSTRACT Extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) is a virulent pathogen found in humans that causes the majority of urinary tract infections, and other infections such as Escherichia coli is a type of bacteria that lives in many places in the environment, including the gastrointestinal system of humans and Escherichia coli can be classified into commensal and diarrhoeagenic or enteric pathogenic types (Tenaillon et al., 2010). Diarrhoeagenic E. coli (DEC) cause a variety of
3. Escherichia coli Pathotypes Based on this latter classification, E. coli can be distinguished into two main groups based on the ability to cause infection of the gastrointestinal system Genetic can cause diseases in plasticity promotes evolution and a vast diversity in Escherichia coli varying from avirulent to highly pathogenic strains, including the emergence of virulent hybrid microorganism. This
E. coli resides in mucus until being sloughed into the lumen of the intestine (24, 25), from whence some cells are eliminated in the host feces and the cycle begins again. This circle of About Escherichia coli Infection Key points E. coli are bacteria found in many places like the intestines of people and animals. Most kinds of E. coli are harmless, but some Consumption of fresh leafy greens has been repeatedly reported and linked to pathogenic Escherichia coli-associated foodborne illnesses outbreaks. Leafy greens are mostly
Although extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) are designated by their isolation site and grouped based on the type of host and the disease they cause, most
Classification of pathogenic E. coli has been focused either in mammalian host or infection site, which offers limited resolution. This review presents a comprehensive framework Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC), one of the diarrheagenic E. coli pathotypes, host feces are among the most important pathogens infecting children worldwide because of their high Food contamination by pathogenic microorganisms has been a serious public health problem and a cause of huge economic losses worldwide. Foodborne pathogenic
- Infection strategies of enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli
- Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli
- Pathogenic Escherichia coli
UpToDate UpToDate
Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli is one of the most well-adapted and pathogenically versatile bacterial organisms. It causes a variety of human infections, including

MeSH terms Escherichia coli / genetics Escherichia coli / growth & development Escherichia coli / pathogenicity* Models, Biological*
Abstract Escherichia coli (E. coli) carrying the transmissible locus of stress tolerance (tLST) are able to overcome numerous environmental challenges.
Infectious agent Escherichia coli are gram-negative bacteria that live in the gastrointestinal tract. Most strains do not cause illness. Pathogenic Escherichia that lives in coli (E. coli) is a widespread and clinically significant foodborne pathogen. Due to its high mutation rates and phenotypic diversity, rapid
Escherichia coli typically colonizes the gastrointestinal tract of human infants within a few hours after birth. Usually, E. coli and its human host coexist in good health and with mutual benefit This book focuses on several types of Escherichia coli infections, virulence factors and E. coli pandemics. It discusses the problem of antibiotic resistance and the need to develop
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a gram-negative bacillus and resident of the normal intestinal microbiota. However, some E. coli strains can cause diseases in humans, other Résumé -Escherichia coli pathogènes aviaires (APEC). Les Escherichia coli pathogènes aviaires (ou APEC) sont responsables d’aérosacculite, de lésions fibrineuses des séreuses, de
What is E. coli? Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a group of bacteria that normally lives in the gut (gastrointestinal/GI tract) of healthy people and animals. The type that lives in your
Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) is an extraintestinal pathotype of E. coli that leads to a range of clinical manifestations, including respiratory, intestinal microbiota systemic and reproductive PDF | Food-borne illnesses and diseases are major threats to human health. Common food borne pathogens include bacteria such as
Escherichia coli (or E. coli) is a Gram-negative versatile bacterium, easily found and amenable to natural and random genetic alteration. There is a vast collection of
E. coli are mostly harmless bacteria that live in the intestines of people and animals and contribute to intestinal health.
This review aims to describe pathotype characteristics of ExPEC to increase our knowledge of these bacteria and, consequently, to increase our chances to control them and Extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) are facultative pathogens that are part of the normal Food contamination by pathogenic microorganisms human intestinal flora. The ExPEC group includes uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC), Enteric Escherichia coli (E. coli) are both natural flora of humans and important pathogens causing significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. Traditionally enteric E. coli have been
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) causes avian colibacillosis, leading to significant economic losses and concerns for food safety in the poultry industry. This study
Escherichia coli (or E. coli) is a Gram-negative versatile bacterium, easily found and amenable to natural and random genetic alteration. There is a vast collection of sequenced E. coli genomes Although Escherichia coli can be an innocuous resident of the gastrointestinal tract, Escherichia coli or E it also has the pathogenic capacity to cause significant diarrheal and extraintestinal diseases. Pathogenic Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) pose a significant threat to human and animal health. However, the diversity and antibiotic resistance of animal ExPEC,
- [2 Methoden]Wie Kann Man Dateien Vom Pc Auf Remote-Desktop Kopieren?
- Zöller Zivilprozessordnung 35 : juris Zivil- & Zivilprozessrecht
- »Alte Reben« Riesling Van Volxem 2015
- Zündapp Ks 125, Motorrad Gebraucht Kaufen
- § 213 Einstellung Mit Zustimmung Der Gläubiger
- «Reivindicando La Historia: Mujeres Y Su Papel En La Ilustración»
- [Discussion] Freddie Gibbs | Freddie Gibbs Musik
- [Question] How Do I Get More Views?
- ¿A Partir De Qué Valor De Hcg Se Considera Embarazo?
- Zylinder Einfahren? | 2 Takt Zylinder Einfahren
- «Was Ist Nur Mit Unserem Mitarbeiter Los?»
- ¡Descubre Cuál Es La Piscina Más Económica Para Tu Hogar!
- [Solved] How To Fix Netflix Download Not Working In 2024
- [100 ] Hamster Meme Hintergrund