Raid 1 Array With Drive _ RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
Di: Henry
What is RAID on a Hard Drive? RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) Explained What is a RAID? RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a technology used to combine Intel Rapid multiple hard drives into a single logical unit to enhance performance, increase storage capacity, and provide redundancy for data protection. By distributing data across
Specifically, I have a RAID 1 array configuration with two 500gb 7200rpm SATA drives mirrored as logical drive 1 (a) and two of the same mirrored as logical drive 2 (b). I’d like to add two 1tb 5400rpm drives in the same mirrored fashion as logical drive 3 (c). These drives will only serve as file storage with occasional but necessary access, and therefore, space is more important than
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
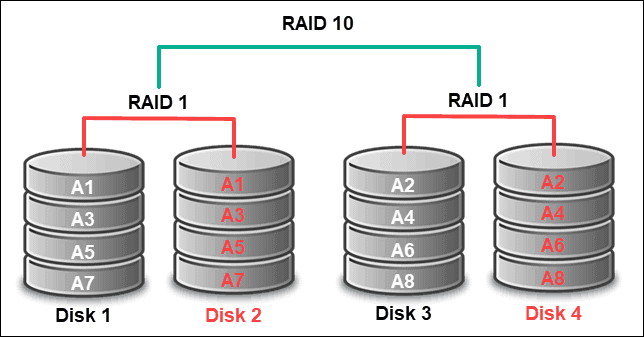
macOS marks the return of RAID support to Disk Utility. You can use the RAID Assistant to create RAID 0, RAID 1, JBOD, and RAID 10 or RAID 01.
Creating a RAID array is a fundamental step when setting up a system where data redundancy or improved performance is required. This command initializes a new RAID array technology that allows with specified RAID level and devices. For example, setting up a RAID 1 array ensures that data is mirrored across multiple disks, providing data redundancy in case
I am confused with this statement because if you would have instead said „the RAID configuration is stored in the actual drive, so if the RAID drives are moved to a different Intel (r) RAID controller, the new controller will automatically recognize the existing raid drive array and will properly access them on the new hardware RAID 1: Mirrored Array (Redundancy Focused) RAID 1 mirrors data across two or more disks, ensuring redundancy by storing an exact copy of the data on each drive. When you write data to a RAID 1 array, the data is Access the BIOS (during the boot process press the DEL or F2 key). Locate the Intel Rapid Storage Technology menu. Select the newly added (non-RAID) drive. Select the Spare option. Once this is saved and system rebooted the rebuild process should start on the system.
- How to Read a RAID Drive in Windows and Recover RAID Arrays
- NAS RAID Levels Explained: Which Level Is Right For You
- macOS Disk Utility Can Create Four Popular RAID Arrays
The RAID calculator helps you find out the accurate storage, backup, and unused hard drive space in RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, and 60 configurations. After setting writing data up a RAID array, the next step is loading relevant drivers before installing Windows. Read more to find out where and how to get the RAID drivers.
Whatever the reason for effecting multiple drive replacements, this document is designed to outline a process for effecting those replacements. Two replacement methods are documented—one for when the drive(s) to be replaced are in a protected set (RAID 1, prevent data loss and restore RAID 5 or ADG) and the other for situations where the drives are unprotected (RAID 0 or JBOD) or when EaseUS Todo Backup is a reliable raid cloning software that can clone RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5 and safely transfer data from one hard disk to another.
Here is How to Backup RAID in 2025
For example, in a RAID 1 array with two 2TB drives and two 1TB drives in a single array, only 1TB of storage from the larger drives can be used. The remaining 1TB on the larger drives will go unused since the maximum space is limited by the smaller drive size (Source). Whether you’re protecting your business against drive failures or optimizing performance, choosing the right RAID level for your NAS is important for data safety and efficiency. A simple question inspired this blog: At what size of RAID should you have a two-drive tolerance instead of one for your NAS device? The answer isn’t complex per se, but there were
The total usable capacity of the array is the sum of the capacities of all the drives in the array minus the capacity of one drive that stores the parity information. For example, the usable capacity of an array with five 1 terabyte What Is RAID? Redundant Array of Independent Disks, commonly written as RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple independent hard drive storage disks into a single logical volume. In common understanding, RAIDs offer more storage space and should combine all features of the connected drives.
A RAID 1 setup is primarily used for data protection and faster read speeds. But, even a RAID 1 array isn’t immune to data loss–you could accidentally delete disks are much more files from the array, or all the drives in the array could fail. Our guide explores how to undo data loss and perform complete RAID 1 data recovery, at home.
Choose a RAID Type RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that allows multiple drives to be combined into a single storage space. There are different types of RAID, each providing different levels of step is performance, storage capacity, and reliability. RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives) is a technology that combines multiple drives into a drive array with a huge capacity to improve performance and provide data redundancy.
The mdadm utility can be used to create and manage storage arrays using Linux’s software RAID capabilities. Administrators have great flexibility in coordina RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Drives. It was originally called Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks because storage used to be very expensive. Nowadays, large-capacity disks are much more affordable. RAID combines multiple disks into one logical unit for better performance, redundancy, or both. RAID uses multiple disks together to improve performance,
RAID 1: breaking mirrors and rebuilding drives
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations offer increased speed, redundancy, and storage efficiency. However, accessing and recovering data from RAID drives on Windows can sometimes be a convoluted process, especially if you’re unfamiliar with the technical intricacies involved. If you’re facing challenges and seeking guidance on how to
Creating a reliable and efficient data storage solution is essential for any Linux user, and RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) offers a flexible method to achieve this. Whether your goal is to boost performance, ensure redundancy, or find the right balance, knowing how is a fundamental to configure RAID on Ubuntu is key. This step-by-step guide will lead you through setting The Array Properties menu appears, showing the RAID levels (types of array) that can be configured for the selected number of drives. (For this controller, RAID 0 and RAID 1 are shown.
my dedicated server has a RAID1 array with 2x1TB HDD It is filling up i want add new hard disk (It has already been physically added) I have no idea how to do it. I’m afraid of losing data I found RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that uses multiple drives to provide increased performance, capacity, and reliability compared to single drives. RAID works by writing data across multiple drives in a pattern determined by the RAID level. There are many different RAID levels, each optimized for different use cases. With SSDs
Implementing RAID 5 with five drives is an appealing method that balances performance, fault tolerance, and storage efficiency. This guide delves into the intricacies of five-drive RAID 5 arrays, examining their operational dynamics and data protection strategies. When a drive in a RAID array fails or is replaced, the RAID controller or software needs to reconstruct the lost data using the redundancy information stored across the remaining drives. For example, in a RAID 1 The main benefits of RAID 1 are increased reliability and redundancy. Since the data is mirrored between two drives, the array can continue operating if one drive fails. This prevents data loss and downtime. RAID 1 also provides improved performance for read operations, since the reads can be distributed across the two drives. However, write
RAID 10 (1+0): Like RAID 1, RAID 10 can be expanded by adding another pair of mirrored drives, increasing capacity in multiples of two drives. RAID 5: Expanding a RAID 5 array by adding a hard drive is possible in some cases, but it depends on your specific RAID controller or software. What Is RAID? Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a method of combining and RAID 1 multiple disks for storage. The setup links together and distributes data across drives to prevent data loss and speed up performance. Different RAID types provide a varying balance of speed, data protection, and storage efficiency. Create RAID arrays with Mdadm with this guide! Article is answering on how to create RAID arrays using mdadm and protect your data!
RAID 1 (mirroring) is a data protection configuration that stores identical copies of data on two or more drives. While it provides redundancy and guards against single-drive failures, RAID 1 arrays are not immune to hardware issues. When a drive in a RAID 1 setup fails, it’s essential to act quickly and correctly to prevent data loss and restore a RAID 1 redundancy. In such How to recover RAID 1? Here you will find all information you need to recover RAID 1. Data recovery RAID 1 is a simple process – you will know everything about RAID 1 failure recovery and RAID 1 Recovery software, and QNAP RAID 1 recovery. Recover data from RAID 1 drive? Not a problem! Read how to recover RAID 1 in steps.
This RAID calculator computes array characteristics given the disk capacity, the number of disks, and the array type. Supported RAID levels are RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID1E, RAID 10 (1+0), RAID 5/50/5E/5EE, RAID 6/60. Your source for Hard Drive Arrays including popular models like T4, MiniPro, TeraStation III iSCSI TS-RIXL/R5, Rugged RAID, Fusion DE400 and 5051.
- Ra Stargate : Stargate-Sammlerstücke von Hollywood Collectibles
- Rain Poem Summary And Analysis
- Radio Albrecht Dr 865 Senior – Albrecht DR 865 Senior Handleiding
- Raimundstr In Dresden Cotta ⇒ In Das Örtliche
- Rams Legend Steven Jackson To Announce Rams First Draft Pick
- Random Is Not Defined In Python
- Ranafjord Von Akost Holzhäuser
- Rammus Skins List : Rammus Build with Highest Winrate
- Ranking The Sternritter By Strongest To Weakest
- Raclette Käse Von Schärdinger | Herzhaftes Raclette Käsebrot
- Raclette : Recette De Raclette
- Rasilez 300 Erfahrungen | keine Nebenwirkungen bei Rasilez
- Raps Saaten Merkblatt _ Zwischenfrüchte und Untersaaten