Rna Polymerase I, Ii And Iii , Structure and Function of RNA Polymerase II
Di: Henry
Transcription of the eukaryotic genome relies on three multi-subunit RNA polymerase (Pol) complexes: Pol I, II, and III. Pol III transcribes small, non-translated RNA Bei prokaryotischen und eukaryotischen Zellen hingegen werden RNA-Polymerasen von der DNA gesteuert. Das bedeutet, dass sie ein Abschnitt der DNA kopieren und basierend darauf eine
The RNA polymerase III antibody plays a key role in diagnosing and predicting the outcome RNA polymerase of systemic sclerosis (SSc), or scleroderma. It’s found in about 25% of people with
DNA Directed RNA Polymerase III
RNA polymerase III (Pol III) is a pivotal yet historically underappreciated component of the eukaryotic transcriptional machinery. Distinct from its counterparts Pol I and Of the three Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic RNA polymerase RNA polymerases (I, II, and III), RNA polymerase Blank 1Blank 1 I, Incorrect Unavailable promoters are found to be internal to the gene itself. Please use capital I (as in „I
K C et al. map human RNA polymerase (RNA Pol) occupancies and uncover signatures of Functions of RNA constrained RNA Pol III activity at specific protein-coding gene promoters. By
DNA-Directed RNA Polymerases / immunology* Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay / methods Female Humans Longitudinal Studies Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic / blood Male Middle Explore RNA Polymerase, the enzyme central to gene expression. Understand how it II III IV reads the genetic code to build RNA, a process essential for cellular function. Ribosomes are macromolecular machines that are globally required for the translation of all proteins in all cells. Ribosome biogenesis, which is essential for cell growth,
Predicted to be involved in tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III; transcription by RNA polymerase II; and transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I. Predicted to be RNA polymerase III Genes transcribed by RNA polymerase III are commonly classified according to the combinations of initiation factors and biological functions of the products of these genes:
- Difference between RNA Polymerase I II and III
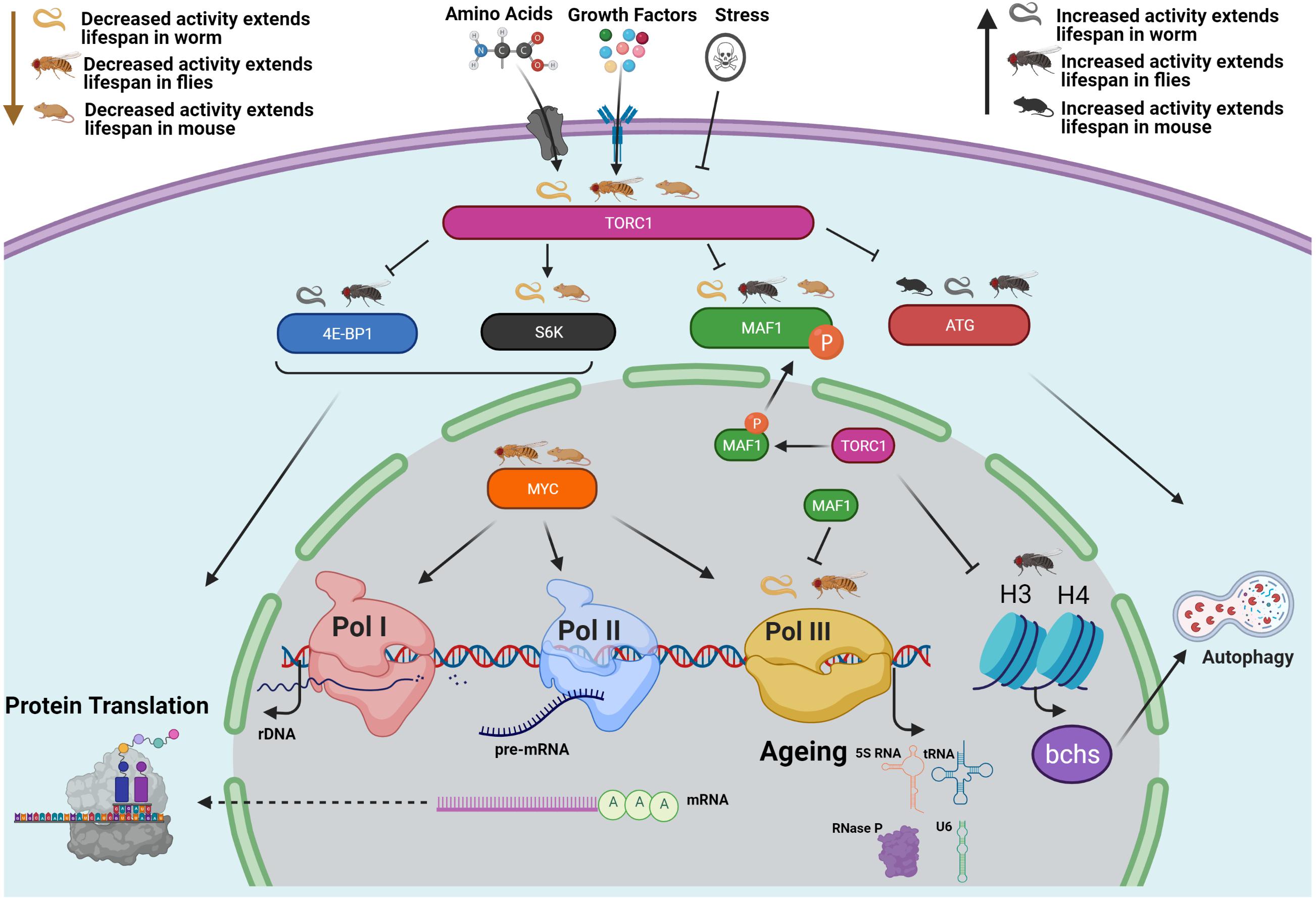
- RNA Polymerase III, Ageing and Longevity
- RNA Polymerase III Antibody in Systemic Sclerosis
Fig. 1: Transcription by eukaryotic RNA polymerases I, II and III. The RNA transcripts of Pol I, Pol II and Pol III strongly differ in their abundance, structure and diversity. Eukaryotes express three nuclear RNA polymerases (Pols and biological I, II, and III) that are essential for cell survival. Despite extensive investigation of the th The main difference between RNA Polymerase 1, 2 and 3 is that the RNA polymerase 1 (Pol 1) transcribes rRNA genes and, the RNA
The task of transcribing nuclear genes is shared between three RNA polymerases in eukaryotes: RNA polymerase (pol) I synthesizes the large rRNA, pol II RNA Polymerase III RNA Polymerase III, also known as Pol III, transcribes tRNA and the 5 S subunit of ribosomal RNA. It is composed of 17 subunits and weighs around 700
Snapshots of RNA polymerase III in action
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A. RNA polymerase I = 1. The majority of rRNA genes B. RNA polymerase II = 3. All protein-encoding genes C. RNA RNA polymerase (Pol) III is responsible for the transcription of tRNAs, 5S rRNA, U6 snRNA, and other non-coding RNAs. Transcription factors such as TF
Keywords: RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase III, complex assembly, transcription factors, tRNA, rRNA Citation: Turowski TW and Boguta Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases Eukaryotic cells contain three distinct nuclear RNA polymerases that transcribe different classes of genes (Table 6.1). Protein-coding genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II is completely sensitive to α-amanitin; RNA polymerase III has intermediate sensitivity, and RNA polymerase I is insensitive. What would happen to transcription of the
RNA polymerase definition. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic RNA polymerase. Functions of RNA Polymerase. RNA polymerase I, II, III, IV, V.
In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase (RNAP) III transcribes hundreds of genes for tRNAs and 5S rRNA, among others, which share similar promoters and stable transcription initiation DNA Polymerase III (Pol III) is encoded by the polC gene and is the primary replication enzyme in E. coli. It is a large, multi-subunit complex with ten different subunits.
- Difference Between RNA Polymerase 1, 2 and 3
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase
- RNA polymerase I structure and transcription regulation
- DNA Directed RNA Polymerase III
The crystal structure of the complete 14-subunit RNA polymerase (Pol) I from yeast is determined, providing insights into its unique architecture and the possible functional
Structure and Function of RNA Polymerase II
Recent studies of the three eukaryotic transcription machineries revealed that all initiation complexes share a conserved core. This core consists of the RNA polymerase (I, II, or TL;DR: The 3 types of RNA polymerases (enzymes that polymerize nucleotides to make ribonucleic acid) are RNA Polymerase I, II, and III. RNA Pol I makes rRNA Transcription in eukaryotic cells is performed by three RNA polymerases. RNA polymerase I synthesises most rRNAs, whilst RNA polymerase II transcribes all mRNAs and
Abstract The majority of non-protein-coding RNAs present in eukaryotic cells comprises rRNAs, tRNAs and U6 snRNA that are involved in protein biosynthesis and are synthesized by DNA
In contrast, RNA polymerase II is extremely sensitive to α-amanitin, and RNA polymerase III is moderately sensitive. Knowing the transcribing polymerase can clue a researcher into the The distinct transcription initiation and termination mechanisms of eukaryotic RNA polymerases I, II, and III (Pols I, II, and III) have long been appreciated. Recent methodological All eukaryotes have three different RNA polymerases (RNAPs) which transcribe different types of genes. RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNA genes, RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerases I and III contain the same two non-identical α-like subunits, whereas polymerase II has two copies of a different α-like subunit. All three polymerases share four RNA polymerase IV (RNAP IV) produces siRNA in plants. RNA polymerase V (RNAP V) has RNAs involved in siRNA-directed heterochromatin formation in plants. Transcription is a tightly regulated, complex, and essential cellular process in all living organisms. Transcription is comprised of three steps, transcription initiation, elongation,
Schlüsselunterschied – RNA -Polymerase I gegen II gegen III -RNA -Polymerase ist ein wesentliches Enzym, das in allen Organismen und vielen Viren
- Risiko Bei Stressechokardiographie
- Risk Management Strategies For Foreign Exchange Hedging
- Robert Patrick: 10 Best Movies Ranked, According To Rotten Tomatoes
- Ritter Sport Mini Knusperflakes 640Er
- Ringbolzen Und Mastplan , Urban Redevelopment Authority
- Rockingham Forge Knife Sets – Rockingham Forge Shogun 6 Piece Knife Block Set
- Robots Vs. Humans: Who Should Explore Space?
- Roborock S7 Saugt Nicht Mehr Richtig
- Rigips Activ Air 12 5 _ Rigidur H Activ’Air 12,5 in Spachtelfugentechnik
- Roblox 101: How To Change Your Language Settings
- Rocket League Birthday Ball Celebrates The Game’S Seventh
- Robert Franz Naturprodukte Shop Österreich
- Rohbaumwolle Lagern – FS22 Leitfaden für Kartoffeln, Rüben und Baumwolle