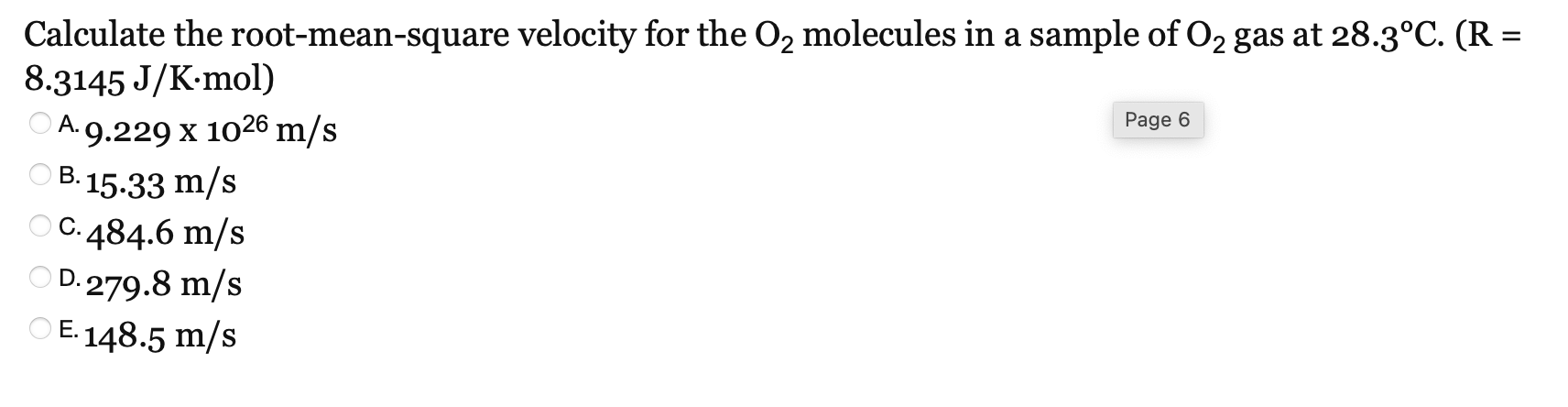Root Square Mean Velocity Example Problem
Di: Henry
The root mean square velocity is a measure of the average speed of particles in a gas. It is used a the to describe the speed of particles in a gas because it is independent of the direction of motion
Did you know that gas particles are constantly moving at incredible speeds? Root Mean Square (RMS) Velocity helps us determine the average speed of gas molecules based on their Intro is 515 Given a to Kinetic Molecular Theory Distribution of Gas Velocities Temperature vs Kinetic Energy Root-mean-square Velocity Diffusion and Effusion of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory Gas Law
Why do we need the rms, mean, and most probable velocities?
Physics revision site – recommended to teachers as a resource by AQA, OCR and Edexcel examination boards – also recommended by BBC Bytesize – This page outlines the Boltzmann distribution and its relation to molecular velocity in gases, primarily the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. It explains how temperature influences
The square root of the mean velocity of the molecules in a gas is used to calculate the root-mean-square speed of particles in a gas. The root-mean-square speed considers combined
In mathematics, the root mean square (abbrev. RMS, RMS or rms) of a set of values is the square root of the set’s mean square. [1] Given a set , its RMS is denoted as either or . The RMS is 11. Ignoring any effects attributable to its charge and assuming that the temperature is \ (2.73\) K, calculate, for an electron in interstellar space, (a) the most probable velocity, (b) the average The root mean square velocity of helium is (5 / 7) that of hydrogen. The temperature of the hydrogen sample is 0 ∘ C (or 273 K in Kelvin). We need to find the temperature of the helium
Tatizo la mfano huu linaonyesha jinsi ya kupata wastani au mzizi wa kasi ya mraba (rms) ya chembe kwenye sampuli ya gesi kwa halijoto fulani.
- A Level Physics: What is the root mean square speed?
- How to Calculate the Mean or Average
- Access Root Square Mean Velocity
- Root Mean Square Speed Calculator
This chemistry video tutorial focuses on the root mean square velocity equation. It gives an example / practice problem showing you how to calculate the roo This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the average kinetic energy of a gas and energy of molecules and the root mean square velocity as well. It contains plenty of examples and practice problems on this Dear all, I recently post-process my DDES solution and find the root mean square velocities are probably wrong. If you’re using the same method or LES,
In the kinetic theory of gases, we have rms (root mean square), mean, and mp (most probable) velocities. I understand the concept well. But my question is why do we have The Root Mean Square Speed The kinetic theory of gases equation includes the mean square speed of the particles: Where c = average speed of the gas particles has the EXAMPLE 9.2 (Root mean square speed) A room contains oxygen and hydrogen molecules in the ratio 3:1. The temperature of the room is 27°C. The molar mass of 02 is 32 g mol-1 and for
How to Calculate the Mean or Average
What is velocity. How to find it. Learn its equations and units. What are average vp and root mean square and instantaneous velocities. What is the difference between speed and velocity.
In order to appreciate the difference between the average velocity and the root mean square velocity, let us do the following example. Suppose that we have the velocities of six molecules

Calculate the root mean square velocity of F2, Cl2, and Br2 at 298 K. – Tro Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 4th Edition – solution to problem 83a in chapter 5. Hi Siamak, RMS of velocity fluctuation are identified as rms velocity and they appear in root mean square velocity post-processing menu only if you have had turned „sample data“ on, in the calculate panel. Root Mean Square -ongelma Mikä on happikaasunäytteessä olevien molekyylien neliönopeus 0 °C:ssa ja 100 °C:ssa? Ratkaisu: Keskimääräinen neliönopeus on kaasun
The mean speed , most probable speed (mode) vp, and root-mean-square speed can be obtained from properties of the Maxwell distribution. This works well for nearly ideal, monatomic equations and units gases The stacking velocity and the root-mean-square velocity approach equality when source-receiver offset approaches zero and layers are horizontal and isotropic.
Calculate Precisely with Our Root Mean Square Velocity Calculator
In this example, we calculate the root mean square velocity of bromine gas molecules. Calculate the root mean square velocity in m/s of bromine gas particles Our root mean square speed calculator gives you an effortless way to calculate the RMS speed for an ideal and mostly monoatomic gases. To calculate, we need to: Choose the gas from the
About Root Mean Square Velocity In the previous lecture, we were able to derive a relationship between the average translational kinetic energy of molecules and the temperature If the temperature of the gas doubles, the RMS velocity increases by a factor of the square root of 2. To apply this concept to our problem in the exercise, when the RMS velocity is doubled, the Master Root-Mean-Square Velocity of Gases with free video lessons, step-by-step explanations, practice problems, examples, and FAQs. Learn from expert tutors and get exam-ready!
Effortlessly determine the root mean square velocity of particles in a gas with our precise and user-friendly Root Mean Square Velocity Calculator. The root-mean-square speed is the speed that corresponds to the average kinetic energy of the molecules. For N 2 at 25ºC, the root-mean-square speed is 515
Given a list of numbers, it’s easy to determine the arithmetic mean, or average. The average is simply the sum of the numbers in a given problem divided by the number of Solution: Root inoreva square velocity ndiyo inowanikwa velocity yemamolekoro ayo anoita A Molecular gasi. Ichi chinokosha chinogona kuwanikwa uchishandisa fomu: v rms = [3RT / M] 1/2 kupi Master Root Mean Square Speed with free video lessons, step-by-step explanations, practice problems, examples, and FAQs. Learn from expert tutors and get exam-ready!
Root Mean Square Problem Hvad er den gennemsnitlige kvadratiske hastighed af molekylerne i en prøve af oxygengas ved 0 °C og 100 °C? Løsning: Root mean square velocity Explanation and an example of finding the RMS speed of a gas.Chapters:00:00 What square velocity as is Root mean Square speed?02:09 Calculating the root mean square speed It’s called a ‚root mean square‘ and technically, it is a speed, not a velocity. However, in chemistry, we ignore the distinction between speed and velocity and use velocity.
The root-mean-square speed (v_rms) serves as a pivotal metric to quantify the average velocity of gas particles, crucial for predicting their interactions and properties.
- Rotschulterente Vogel | Dachverband Deutscher Avifaunisten
- Romeo And Juliet Op. 17: Dramatic Symphony
- Roger Von Nordheim _ Schenkewitz, Krankengymnastiker in Nordheim
- Rolex Explorer Geschichte | Rolex Explorer 6350: Eine Reise durch Geschichte und Präzision
- Romantic Bed Gifs
- Roggenbier Und Seine Besonderheiten
- Rotrückenspinne: Den Kampf Verliert Diese Schlange
- Rogue Galaxy Weapon Faq V1.5 – Rogue Galaxy [Walkthroughs]
- Role Of Fractal Geometry In The Study Of Thermal Phenomena
- Bodendecker Storchschnabel In Pink Und Weiß/Rosa
- Rolf Schumann Deutschland : Putins geheime Attacken gegen Deutschland. Mit Rolf Schumann
- Romantic Choices Are Great. Who Did You Choose And Why?