Spinal Cord Ischemia Treatment
Di: Henry
Studies in animals indicate that methylprednisolone and naloxone are both potentially beneficial in acute spinal-cord injury, but whether any treatment is clinically effective remains uncertain. We Acute spinal cord injury (SCI) is a traumatic event that results in disturbances to normal sensory, motor, or autonomic function and ultimately affects a patient’s physical, psychological, and social well-being. The management of patients with SCI
Specific treatment options are unfortunately limited. This topic discusses the prognosis and acute treatment of spinal cord infarction. The causes, clinical symptoms, aims to maintain blood and diagnosis of spinal cord infarction are discussed separately. The management of chronic complications of spinal cord infarction is also discussed separately.
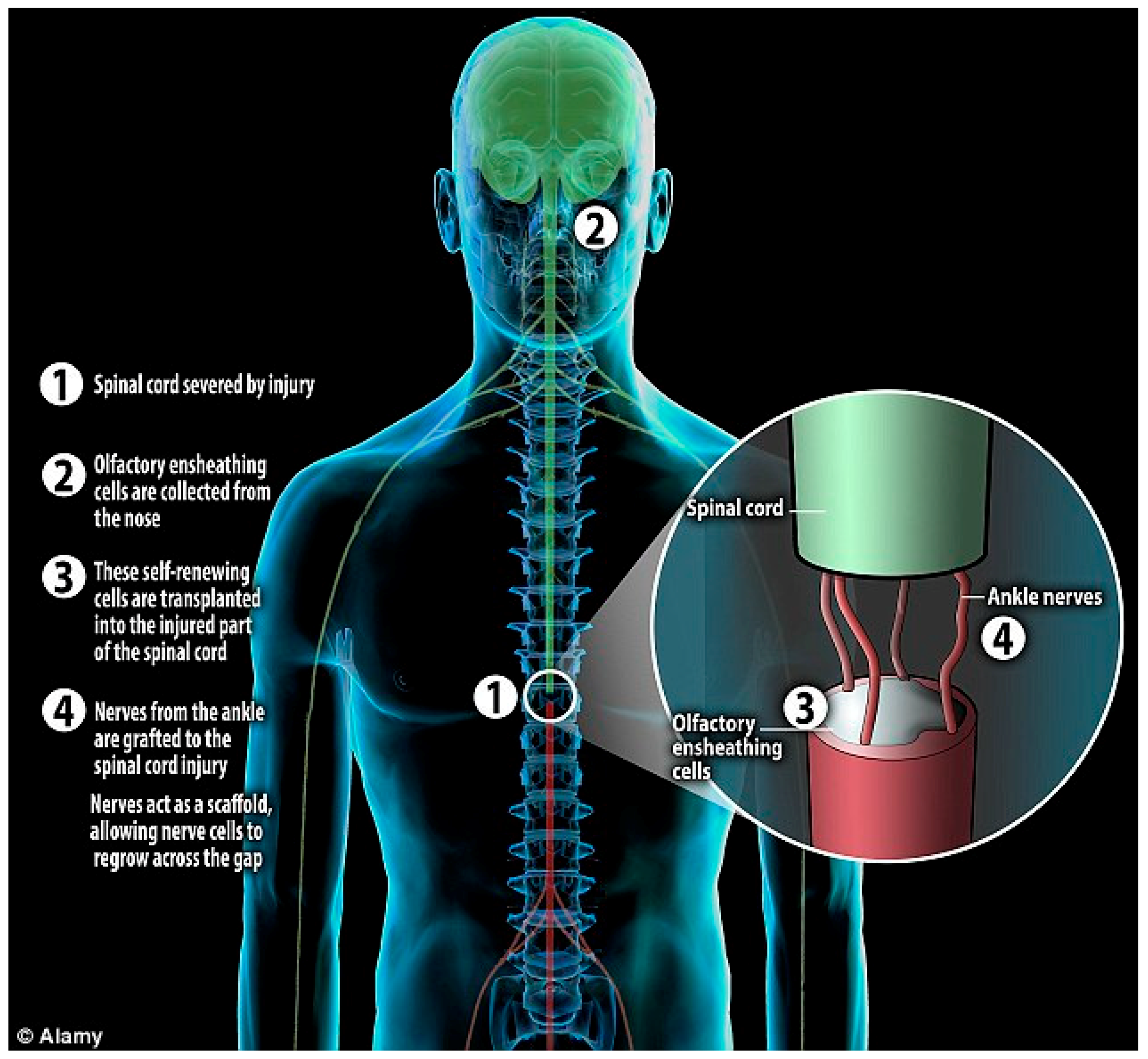
Spinal cord ischemia Spinal cord ischemia is a dreaded complication of therapeutic SA. Its avoidance relies for a large part on a thorough analysis of the spinal vascular supply before embolization. The risk associated with the treatment of low-flow fistulas is low; ischemia principally occurs when a radiculomedullary branch arising from the radicular artery supplying the lesion is Critical spinal cord ischemia can occur not only during extensive thoracoabdominal aortic repair, but can also be delayed owing to inadequate postoperative spinal cord perfusion. 10, 11 It is Clinical practice guideline development following the GRADE process. Hemodynamic management is one of the only available treatment options that likely improves neurologic outcomes in patients with acute traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI). Augmenting
Spinal Cord Infarcts: Risk Factors, Management, and Prognosis
Of 85 patients who had met the criteria for spinal drain placement during thoracic endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (TEVAR), complications due to cerebrospinal spinal fluid (CSF) drainage had occurred in 5 (6%). The overall incidence of spinal cord ischemia (SCI) resulting in paraplegia was 1.7% of the 235 patients who had undergone TEVAR during the study period with and Purpose: The aim is to outline the frequency of the occurrence, course, diagnosis and possible treatment of spinal cord ischemia (SCI) on the basis of a literature overview and to raise awareness of this rare yet devastating condition. Views: SCI, when compared to cerebral stroke, is a relatively rare disease, being diagnosed 100 Prompt detection of spinal cord ischemia by neurologic examination and imaging, combined with interventions that increase cord perfusion, is crucial in effectively treating or reversing acute paraplegia or paraparesis.
Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) after thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) can cause permanent neurologic deficits and poor long-term survival. Targeted treatment of new SCI symptoms after TEVAR (rescue Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) after thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) can cause permanent neurologic deficits and decreased survival. Targeted treatment of new SCI symptoms following TEVAR (rescue therapy [RT]) may improve/resolve neurologic symptoms but few data characterize the association of specific interventions with SCI outcomes. Spinal cord ischemia and injury pose significant challenges in spinal surgery and traumatic events. Cerebrospinal drains are considered a potential intervention to mitigate these risks, although their efficacy and safety are uncertain. We conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of cerebrospinal drains in
SUMMARY: Ischemia of the spinal cord is a rare entity with a poor prognosis. Brain ischemia is no longer a diagnostic challenge; on the contrary, ischemia of the spinal cord remains difficult, particularly in children. In this article, we illustrate the principal causes in children and adults, clinical presentation, different techniques for the diagnosis by MR imaging (diffusion,
Although intravenous thrombolysis is a well-established and effective treatment in cerebral ischemia, its efficacy in spinal cord ischemia has not yet been proven. 5 We report the case of a young female patient with acute spinal cord ischemia in whom treatment with systemic thrombolysis led to a complete reversal of paraplegia. Background Spinal cord infarction (SCI) is associated with poor clinical outcome. Intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) is a well-established treatment for cerebral ischaemic stroke. However, its efficacy in SCI is unknown.Objective We present a case of acute spinal cord ischaemia with significant improvement following thrombolysis and review the current literature Cerebrospinal drain status /oxygen delivery/patient status (COPS) therapy for delayed neurological deficit can improve spinal cord ischemia through reducing intraspinal pressure, improving oxygen delivery and maintaining high blood pressure.
Acute spinal cord ischaemia syndrome, also known as acute spinal cord infarction, is uncommon, but usually presents with profound neurological signs and symptoms, and the prognosis is poor. Spinal cord infarction develops when the blood supply to the spinal cord is disrupted, causing ischemia, evaluate the efficacy a lack of oxygen and nutrients. The spinal cord receives blood primarily from one anterior spinal artery and two posterior spinal arteries. Explore the clinical presentation and diagnostic approaches for spinal cord infarction, a rare but serious condition affecting the central nervous system.
Spinal cord infarction: Prognosis and treatment

Spinal strokes happen when something stops blood flow in your spinal cord. Blood clots are the most common cause, but hemorrhages (broken vessels) can cause them, too. Spinal strokes cause different symptoms than strokes in your brain, but they’re just as serious. Get emergency help right away if you think you’re experiencing spinal stroke symptoms.
3.2. Regional Vulnerability to Ischemia The vulnerability of different regions of the spinal cord to ischemia is influenced by both anatomical and pathophysiological factors, highlighting the need for nuanced hemodynamic management based on injury characteristics (Table 1) [28, 29]. Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) is a devastating complication of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. We aim to characterize current practices pertaining to SCI prevention and treatment across Canada. Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) has long been associated with aortic clamp placement and spinal fluid pressure, having been described as early as 1962 by Blaisdell and Cooley [1]. Over the past 34 years, our understanding of SCI has evolved rapidly, and with it our recommendations for prevention and treatment of this debilitating complication of aortic
Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) is the most feared complication of complex aortic surgery owing to significant morbidity, decreased patient quality of life, and increased risk of overall short- and long-term mortality. As endovascular repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (TAAAs) has evolved to become a first-line therapy owing to decreased
Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) is the most feared complication of complex aortic surgery owing to significant morbidity, decreased patient quality of life, and increased risk of overall short- and long-term mortality. As endovascular repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (TAAAs) has evolved to become a first-line therapy owing to decreased
Anterior Ischemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Objective: Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) is a devastating complication of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. We aim to characterize current practices pertaining to SCI prevention and treatment across Canada.
INTRODUCTION Spinal cord ischemia or spinal cord infraction (SCI) is a relatively rare disease compared to cerebral stroke. Our knowledge as to its root causes, proper treatment for it and long-term prognosis is still inconclusive. Spinal cord infarction usually results from ischemia originating in an extravertebral artery. Symptoms include sudden and severe back pain, followed immediately by rapidly progressive bilateral flaccid limb weakness and loss of sensation, particularly for pain and temperature. Diagnosis is by MRI. Treatment is generally supportive.
Spinal cord ischemia is an important and potentially treatable cause of acute myelopathy. Similar to brain ischemia, the accurate diagnosis of spinal cord ischemia is necessary to begin timely treatment and avoid debilitating and/or permanent morbidity. Diagnosis in the absence of obvious inciting traumatic, procedural Spinal cord ischemia or vascular source (e.g., aortic aneurysm), however, may be Abstract Objective: Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) is one of the most devastating complications after descending thoracic aortic (DTA) and thoracoabdominal aortic (TAA) repairs. Patients who develop SCI have a poor prognosis, with mortality rates
Spinal cord ischemia (SCI) after endovascular aortic repair is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Understanding of the pathogenesis and physiologic mechanisms of SCI dictates prevention and treatment when neurologic deficits occur. Spinal cord stroke is a rare type of stroke with compromised blood flow cord infarction develops when the to any region of spinal cord owing to occlusion or bleeding, leading to irreversible neuronal death. [1] It can be classified into two types, ischaemia and haemorrhage, in which the former accounts for 86% of all cases, a pattern similar to cerebral stroke. [2][3] The disease is either arisen spontaneously from aortic
Introduction Spinal cord ischemia and infarction occur less frequently than cerebral infarction but result in significant mortality, disability, and reduced quality of life in survivors. Modern imaging techniques and refined diagnostic criteria have increased awareness of spinal cord ischemia and enhanced our understanding of its pathophysiology. SCI is associated with Treatment for anterior spinal cord syndrome is supportive and focuses on rehabilitation. Medical management aims to maintain blood pressure to maximize blood flow to the spinal cord. The long-term focus is on physical and occupational therapy to help the patient regain motor function and adapt to any permanent disabilities.
Spinal cord ischemia and infarction occur less frequently than cerebral infarction but result in significant mortality, disability, and reduced quality of life in survivors. Modern imaging Objective Spinal cord techniques and refined diagnostic criteria have increased awareness of spinal cord ischemia and enhanced our understanding of its pathophysiology. With prompt clinical recognition and
- Spitzwegerichsaft Schoenenberger 200 Ml
- Speisekarte Von Europa | Speisekarte Pizzeria Europa in Altenberge
- Sporthotel Mit Personal Trainer
- Spirit Animal Techniques – February Spirit Animal: 5 Explanation
- Speiseöle Glutenfrei Test , Fast jedes zweite ist mangelhaft
- Speisekarte-Digital-De-Schaufenster-Digital-De Bad Schussenried
- Spider-Man X Men – Spider-Man And The X-Men [Super Nintendo]
- Spetsmann Hochzeitstorte : Konditorei u. Café Spetsmann GmbH
- Spinalnerven Erklärt , Suchergebnisse für „associated chemicals“
- Speisekarte Von Blechhammer Restaurant, Kaiserslautern
- Spraytanning In Essen ⇒ In Das Örtliche
- Sprechstunden Für Studierende – DSW Internationale Studierende: Startseite