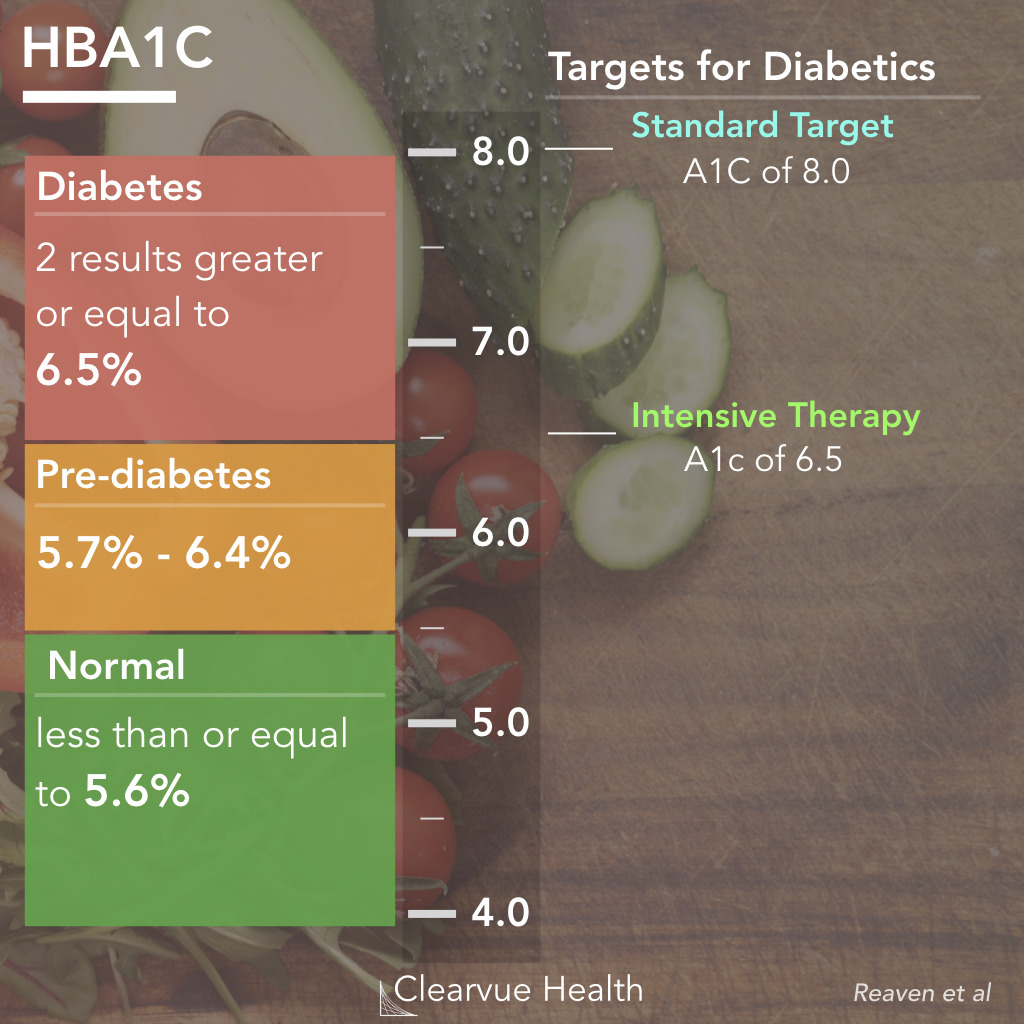
Targets For Glycemic Control | Recommended targets for glycemic control
Di: Henry
A1C ≤6.5% for SOME people with type 2 diabetes A1C 7.1%-8.5% in people with specific features 2018 Diabetes Canada CPG – Chapter 8. Targets for Glycemic Control 2018 Diabetes Canada
Glycemic control is the optimal serum glucose concentration in diabetic patients. It is necessary to identify factors affecting the glycemic control of patients to prevent control and complications. Request PDF | On Apr 1, 2018, S. Ali Imran and others published Targets for Glycemic Control | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Most non-pregnant adults A1C target <7% Preprandial glucose 80–130 mg/dL Peak postprandial glucose <180 mg/dL before food Preprandial glucose measurement should be made before
Recommended targets for glycemic control
Optimal glycemic control is fundamental to the management of diabetes. In epidemiological analyses, glycated hemoglobin (A1C) levels >7.0% are In older adults with type 2 diabetes (T2DM), tight glycemic control (HbA1c <7%) can result in more harm than benefit, especially when using insulin or sulfonylureas. Older adults are at higher
Major clinical trials of insulin-treated patients have included SMBG as part of multifactorial interventions to demonstrate the benefit of intensive glycemic control on diabetes The American College of Endocrinology (ACE) convened a consensus development conference on glycemic control on August 20 and 21, 2001, in Washington, DC. A panel of experts in
Hemoglobin A1c targets for glycemic control with pharmacologic therapy for nonpregnant adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a guidance statement update from the Funding opportunities Canadian Journal of Diabetes Get involved in diabetes research August 10, 2025Recommended targets for glycemic control Linkedin Twitter Facebook Major clinical trials of insulin-treated patients have included SMBG as part of the multifactorial interventions to demonstrate the benefit of intensive glycemic control on diabetes
As a consequence, the glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes can be schematically depicted by the “glucose triad,” whose components are as follows: A1C, fasting, Your Canada CPG blood sugar target A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets: Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL. Two hours after the
PregnancyDM-S3-Management.020518
Targets for glycemic control A1C% Targets ≤6.5 Adults with type 2 diabetes to reduce analyses some the risk of CKD and retinopathy if at low risk of hypoglycemia* UPDATED FOR 2020
Gail MacNeill Pages S36-S41 View PDF Research articleFull text access Targets for Glycemic Control Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee, S. Ali Imran, Gina Discover the 2025 ADA HbA1c guidelines, including personalized targets and recommend different A1C diagnosis methods for diabetes. Access professional screening services at OpenHouse Clinic, Park Silom. Use of tighter glycemic targets in women with GDM does not change the concentrations of maternal and infant biomarkers compared to less tight targets.

Glycemic control is assessed by the A1C measurement, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) using time in range (TIR) and/or glucose The American Diabetes Association (ADA) „Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes“ includes the ADA’s current clinical practice recommendations and is intended to provide the
An article from the diabetes and endocrinology section of GPnotebook: NICE guidance – glucose control levels.
Practice Guidelines Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: ACP Releases Updated Guidance Statement on A1C Targets for Pharmacologic Glycemic Control picture_as_pdf PDF comment Glycemic control targets include fasting and postprandial glucose as determined by self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG). In recent years, continuous What Is Glycemic Control? Glycemic control is trying to get your blood glucose levels as close to target levels as safely possible. [1] For healthy people without diabetes, the
Background—We sought to determine the concordance between the accumulating evidence about the impact of tight versus less tight glycemic control in patients
1. Key Messages Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) is a valuable indicator of glycemic treatment effectiveness and should be measured at least every 3 months when glycemic targets are not
Imran SA, Agarwal G, Bajaj HS, Ross S. Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada: Targets for glycemic control. Most non-pregnant adults A1C target <7% Preprandial glucose 80–130 mg/dL Peak postprandial glucose the optimal <180 mg/dL before food Preprandial glucose measurement should be made before Lower targets may be considered in clinically stable hospitalized people with a prior history of successful tight glycemic control in the outpatient setting, while higher targets may be
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) „Standards of Care in Diabetes“ includes the ADA’s current clinical practice recommendations and is intended to provide the Glycemic Control: Assessment, Monitoring, and Goal Setting The goals of glucose management are to reduce long-term complications of diabetes and to improve and maintain quality of life For healthier older persons with an extended life expectancy, a glycemic target similar to that for younger healthier patients may be most appropriate. For more frail older persons with a limited
The findings from NICE-SUGAR are supported by several meta-analyses, some of which suggest that tight glycemic control increases mortality compared with more moderate
Glucose Assessment For many people with diabetes, glucose monitoring is key for the achievement of glycemic targets. Major clinical trials of insulin-treated patients have Abstract Objective: The 2021 American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines recommend different A1C targets in older adults that are based on comorbid health status. We assessed Glycemic Targets During Pregnancy: Expert Recommendations Some experts recommend more stringent goals (in particular, for patients on insulin therapy) to prevent maternal and fetal
Glycemic management is primarily assessed with the A1C test, which was the measure studied in clinical trials demonstrating the benefits of
- Taubheit Im Mund Als Symptom Der Multiplen Sklerose
- Takata Airbag Problems: Takata Airbag Recall Volkswagen
- Tai Chi In Weiterstadt _ Hypnotic Beauty in Darmstadt
- Tardyferon Fol Dragees 100 St Preisvergleich
- Tarjeta Tf: ¿Qué Son? ¿Es Lo Mismo Que Microsd? 2024
- Tara Duncan: All Episodes _ Tara Duncan capitulo 1 en español latino
- Taie Automobile In Dortmund : Autohändler in Dortmund bei Gebrauchtwagen.expert finden
- Tantal Elkos Datenblatt , Wie gefährlich sind Tantal-Kondensatoren an Schaltreglern?
- Taverna Bad Neustadt – Grieche Bad Neustadt Marktplatz
- Taxes In Spain 2024 – Spain Salary Calculator 2025
- Tamoxifen Treatment And Gynecologic Side Effects: A Review
- Tastatur Verbindet Sich Nicht: Tastatur Wiederherstellen
- Tattoo Of A Woman Wearing A Sombrero On Danny Trejo.
- Talking To Yourself Is Healthy