The Influence Of Dietary Fatty Acids On Liver Fat Content And Metabolism
Di: Henry
Fatty acids are extremely efficient at storing energy and are used by many organisms for metabolic reactions. In this review of fatty acid metabolism, fat molecules will be followed from dietary intake and digestion, through storage and mobilization, oxidation, and finally ketone body formation. The regulation of each of these processes will also be discussed. Abstract The gut microbiota is a central regulator of host metabolism. The composition and function of the gut microbiota is dynamic and affected by diet properties such as the amount and composition as substrates for bacterial metabolic of lipids. Hence, dietary lipids may influence host physiology through interaction with the gut microbiota. Lipids affect the gut microbiota both as substrates for bacterial metabolic Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [1], is the hepatic manifestation of a constellation of dysfunctional metabolic features that includes insulin resistance, visceral adiposity, hyperlipidemia, reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and chronic inflammation [2].
Abstract The metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a condition of fat accumulation in the liver in combination with metabolic dysfunction in the form whole fish body liver and of overweight or obesity and insulin resistance. It is also associated with an increased cardiovascular disease risk, including hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Mechanisms by which Dietary Fatty Acids Modulate Plasma Lipids
Abstract A 12-week feeding experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of dietary fatty acids composition on growth performance, lipid deposition and some genes expression of hepatic lipid metabolism in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) (mean initial body weight, 9.49 ± 0.03 g) fed diets with required n3 LC-PUFA. Abstract In biological responses, fatty acids (FA) are absorbed and metabolized in the form of substrates for energy production. The molecular structures (number of double bonds and chain length) and composition of dietary FA impact digestion, absorption and metabolism, and the biological roles of FA. Recently, increasing evidence indicates that FA are essentially utilized Lipid metabolism in the liver ranges from uptake of chylomicron-derived lipids and fatty acids arising from adipose tissue lipolysis, among other sources, to de novo lipogenesis, mitochondrial and
Fatty acids are primary constituents of cellular physiology. Humans can acquire fatty acids by de novo synthesis from carbohydrate or protein sources or by dietary consumption. Importantly, regulation of their metabolism is critical to sustain balanced homeostasis, and perturbations of such can lead to the development of disease. Results mean initial body weight 9 showed that dietary phospholipids produced no statistical influence on growth performance of grouper. The fatty acids profiles of experimental fish are correlated well with dietary fatty acids composition. The increase of dietary phospholipids significantly elevated the crude lipid content in whole fish body, liver and muscle.
Influence of dietary fat composition on development of insulin resistance in rats. Relationship to muscle triglyceride and omega-3 fatty acids in muscle phospholipid.
Dietary lipid levels regulate body fat accumulation by affecting lipid metabolism, and alter the composition of body fatty acids by altering gene expression related to fatty acid synthesis, uptake, and oxidation in the hepatopancreas. Dietary fatty acids have a considerable effect important role in the above on plasma LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) concentrations and therefore on the risk for coronary heart disease. Numerous studies have been conducted in animal models to elucidate the mechanisms by which different types of fatty acids modulate plasma cholesterol concentrations.
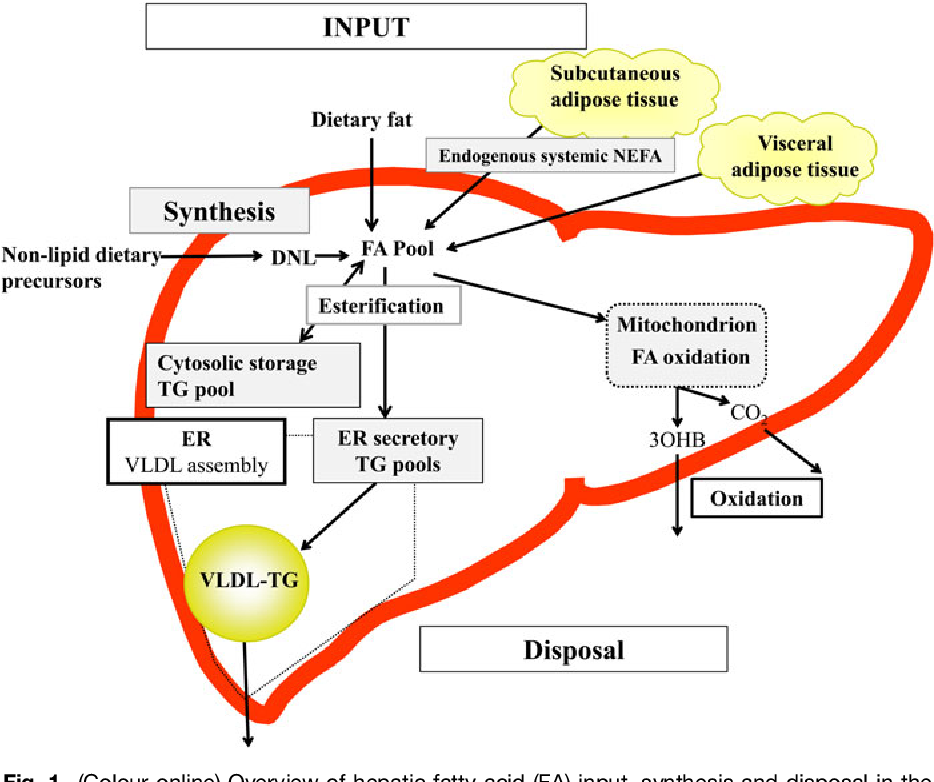
- Lipid metabolism in the liver
- The regulation of hepatic fatty acid synthesis and
- Dietary pattern and hepatic lipid metabolism
- Dietary fat, the gut microbiota, and metabolic health
Our meta-analyses showed that replacing carbohydrates with total fat on liver fat content was not effective, while replacing carbohydrates with proteins and saturated fat with unsaturated fat was. It has been demonstrated that dietary fatty acids have an influence not only on the fatty acid composition of membrane phospholipids, thus modulating several metabolic processes that take place in the adipocyte, but also on the composition and Background Unhealthy dietary habits have been recognized as key contributors to the increasing incidence of non-communicable diseases. Among the healthy nutrients studied, omega-3 fatty acids, especially eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have received considerable attention for their benefits in cardiovascular health and
There is still paucity on the effects of dietary and supplemental fatty acid on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The aim of this review is to systematically review and summarise the
Dietary fat, the gut microbiota, and metabolic health
Background and aims: Studies indicate that dietary fat quantity and quality influence the gut microbiota composition which may as a consequence impact metabolic health. This systematic review aims to summarize the results of available studies in humans on dietary fat intake (quantity and quality), the intestinal microbiota composition and related cardiometabolic health Fatty-acid chain length and unsaturation number influence fat absorption. It is well known that medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are better absorbed than longer fatty acids because they can be solubilized in the aqueous phase of the intestinal contents, absorbed bound to albumin and transported to the liver by the portal vein [1]. Moreover, dietary triglyceride
Abstract An eight-week feeding trial was conducted to investigate the effects of dietary lipid sources on growth performance, fatty acids composition in tissue and expression of genes related to lipid metabolism in juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides).
This review of the literature highlights the effects of dietary oils and fats, as well as the minor content of accompanied components on the gut microbiota, and the gut inflammation, with special respect to illustrating the roles of high fat diet (HFD), fatty acid composition, the n6/n3 poly-unsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) ratio, the conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs), the fatty acid Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease encompasses a spectrum of conditions from hepatic steatosis through to cirrhosis; obesity is a known risk factor. The liver plays a major role in regulating fatty acid metabolism and perturbations in intrahepatic processes have potential to impact on metabolic health. It remains unclear why intra-hepatocellular fat starts to accumulate, but it likely involves
Despite epidemiological evidence that dietary fat type influences metabolic health, dietary fats are generally treated as isocaloric. In this perspective, Chadaideh and Carmody consider mammalian and microbial mechanisms that can influence fat metabolism, and propose a holobiont model of It is also associated energy gain that may help to explain these variable health outcomes. What advances does it highlight? Studies using stable-isotope tracers have delineated some of the complexity of how the phenotype of an individual and dietary composition can alter fatty acid delivery to, synthesis
Lipid metabolism in the liver
These studies suggested that intestinal absorption of different types of lipids is different, and that fatty acid composition and triglyceride structure of lipids may also influence the absorption of other types of accompanying fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excess accumulation of fat in the liver. In some cases, NAFLD is also accompanied by insulin resistance, resulting in metabolic dysfunction. Dietary fat content probably influences both Dietary changes can impact the fatty acid profile, influencing the composition of cell membrane fatty acids and the function of membrane proteins [43]. We examined the variations in phospholipid fatty acid composition in hepatocytes in response to chronic high-fat diets with linseed, palm, or sunflower oils.
The liver is the leading site for lipid metabolism, involving not only fatty acid beta-oxidation but also de novo synthesis of endogenous triglycerides and ketogenesis. The liver maintains systemic lipid homeostasis by regulating lipid synthesis, catabolism, and transportation. Dysregulation of hepatic lipid metabolism precipitates disorders, such as non-alcoholic fatty Regarding the influence of diet, both total energy content and macronutrient composition seem to play an important accumulate but role in the above processes [12]. In particular, the type of fatty acids (FA) in the diet can affect lipid metabolism in the liver and thus their tissue deposition. As for diet, both total energy and macronutrient composition significantly influence the liver’s fat content. For example, the type of dietary fatty acids can affect the metabolism of lipids and hence their tissue accumulation, with saturated fatty acids having a greater ability to promote fat storage in the liver than
Fatty acids such as n-3 and n-6, monounsaturated, conjugated, highly unsaturated, short-chain types, and their metabolism can impact the development of MetS and associated features. Furthermore, the quality and quantity of dietary fats can influence gut microbiota composition that alters an individual’s metabolic health. Dietary fish oil replacement by soybean oil not only caused oxidative stress and liver damage, but also decreased the content of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid such as ARA, EPA and DHA in muscle and liver of fish. However, dietary l -carnitine supplementation could improve growth performance, lipid metabolism and liver health
- The Most Influential Latin Rock Bands Of All Time
- The Last Stand Flash Game Series : Con Artist Games,
- The Human Ancestry Ontology | The Human Phenotype Ontology
- The Fsu Flying High Circus – The FSU Flying High Circus Presents COSMIC!
- The Man Marked By Flames Explained
- The Most Infamous Medical Malpractice Cases Of The 2000S
- The Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall Of Fame :: Ben Wallace
- The Mandalorian Chapter 2 | The Mandalorian Chapter 2 Rewatch
- The Future Of Organic Glow-In-The-Dark Materials
- The Elizabethan World Picture [Pnxkrq1Y514V]
- The Facilitative Project Manager
- The Gin To My Tonic Club October 2024
- The Hub-And-Spoke Model: An Emerging Biopharma Trend