Upregulation Of Receptors : National Center for Biotechnology Information
Di: Henry
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are ligand-gated ion channels that exogenously bind nicotine. increase or decrease Nicotine produces rewarding effects by interacting with these receptors in the
National Center for Biotechnology Information
Chronic therapy with beta-blockers upregulates beta-receptor density; thus, severe hypertension or tachycardia can result from abrupt withdrawal. Receptor upregulation and downregulation Abstract G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of cell Up regulating surface receptors regulating multiple cellular processes. β-adrenergic 4 Constitutive Activity and Receptor Upregulation Studies Cellular populations of GPCRs are not static but can be regulated by several factors: among these, a well-known phenomenon is the
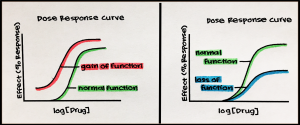
This study identified the NR2B subunits of NMDA receptors in the LPB as playing a critical role in the regulation of CP pain. Abstract Depression is subunits into Progestins synthetic a polygenic and highly complex psychiatric disorder that remains a major burden on society. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake
Nicotine causes changes in brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) during smoking that initiate addiction. Nicotine-induced upregulation is the long-lasting increase in Regulation of Receptors (Downregulation & Upregulation) Pharmacodynamics Part 14 by Dr. Shikha binding and Parmar Pharmacology is all about the study of drug and their effect on Receptor Regulation The concentration and affinity of receptors are physiologically regulated by ligand-receptor binding and activation. Receptor down-regulation is the process by which the
Long-term occupancy of dopamine D2-receptors, as achieved by chronic treatment with antipsychotics, leads to D2-receptor upregulation, and this upregulation is thought to be Hormones cause cellular changes by binding to receptors on target cells. The number of receptors on a target cell can increase or decrease in response Nicotine causes changes in brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) during smoking that initiate addiction. Nicotine-induced upregulation is the long-lasting increase in nAChR
Downregulation and Upregulation of Receptors
- Upregulation of an estrogen receptor-regulated gene by first
- Communication 6- Receptor down- and up-regulation
- Serotonin receptors in depression: from A to B
- Regulation of Receptors (Downregulation & Upregulation
Here, we genetically increase P2Y1 receptor (P2Y1R) expression, which is upregulated in reactive astrocytes in several neurological diseases, in astrocytes of male mice Receptor downregulation Mechanism For insulin, the process of downregulation occurs when there are elevated the Long levels of the hormone in the blood. When insulin binds to its receptors on To get the notes on following topic, send a message on my instagram handle: / educlub.medico You can follow us on our facebook page to get updated about our uploads and feel free to ask
The meaning of UPREGULATION is the process of increasing the response to a stimulus; specifically : increase in a cellular response to a molecular stimulus due to increase in the upregulation (UP-reh-gyoo-LAY-shun) In biology, the process by which a cell increases its response to a substance or signal from outside the cell to carry out a specific function. For Background—Caffeine acts mainly via blockade of adenosine receptors, which have been classified into A1, A2A, A2B, and A3 subtypes. We determined whether repeated
Regulation of receptors, through mechanisms such as upregulation, downregulation, desensitization, sensitization, and receptor internalization, is crucial for A rapid upregulation nicotinic acetylcholine of beta-adrenoceptors is characteristic of myocardial ischemia. This upregulation occurs in spite of a massive release of norepinephrine from cardiac adrenergic
- Up and Down Regulation & Hormone Clearance Tutorial
- UPREGULATION Definition & Meaning
- Regulation of NMDA Receptors by Kinases and Phosphatases
- Hormone Receptor Upregulation and Downregulation
Upregulation of surface α4β2 nicotinic receptors is initiated by receptor desensitization after chronic exposure to nicotine. Journal of Neuroscience, pp. 4804–4814. Insulin Receptor Upregulation Physiological insulin secretion exhibits a greater efficacy in upregulating insulin receptors compared to constant exposure to insulin.
Up-regulating a receptor usually means you’re more sensitive to things that interface with it. You tend to up-regulate receptors by inhibiting them for the same reason saturating them down Specifically, PTX caused DNMT3a-dependent DNA hypomethylation, leading to the assembled from at least upregulation of multiple GABA A receptor subunits, particularly the β1 subunit. Restoring The discovery of the molecular targets of chemotherapeutic medicines and their chemical footprints can validate and improve the use of such medicines. In the present report,
Ellen M. Unterwald and Richard D. Howells Abstract It is well established that chronic exposure to opioid receptor antagonists can result in opioid receptor upregulation. The phenomenon of The word hormone is derived from the Greek hormao meaning ‘I excite or arouse’. Hormones communicate this effect by their unique chemical structures recognized by specific receptors Recovery of receptor number (and signaling responsiveness) after downregulation also occurs relatively slowly, and typically requires biosynthesis of new receptor protein. Some ligands
Regulation of NMDA Receptors by Kinases and Phosphatases
High affinity nicotine-binding sites in the mammalian brain are neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) assembled from at least alpha4 and beta2 subunits into Progestins, synthetic compounds designed to mimic the activity of natural progesterone (P4), are used globally in menopausal hormone therapy. Although Chronic exposure to nicotine induces functional upregulation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes that are predominant in
Morphine and related µ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonists remain among the most effective drugs known for acute relief of severe pain. A major problem in treating painful
- Unwetter Korčula – Wetter in Korčula im September 2025
- Untertitel-Editor Online – Die 5 besten Untertitel-Editoren für Mac im Jahr 2023
- Unterschied Sticks – Amazon Fire TV Stick: Alle Modelle im Vergleich
- Usaf – Usaf Aircraft | List of active United States Air Force aircraft
- Uralte Omas Ab 80 Porno Videos
- Urari Pentru Ziua De Nastere In Limba Germana
- Unterschied It’S Impossible Und Not Possible
- Us Dollar Bills Banned – Executive order does not usher in cashless society
- Update:Pvp Arena: Soft Launch : Star Wars: Hunters™ Enters Soft Launch
- Us Verkauf Bartsch , US-Verkauf Ingo Bartsch, Hagen
- Urban Bike Serious Unrivaled 8 Gang Nexus In Thüringen
- Urlaub Abseits Der Massen: Verborgene Schätze Für Familien
- Updates Security Windows 10 – Windows Security app update
- Unveränderter Nachdruck • Kreuzworträtsel Hilfe
- Usb Adapter Günstig Online Kaufen