What Is Audit Risk? – Audit Risk: Assessment and Mitigation
Di: Henry
Risk of Material Misstatement Overview Risk of material misstatement is the risk that financial statements contain material misstatement but the internal control cannot prevent or detect Audit Risk Assessment (ISA 315): A Simple Explanation What is Audit Risk Assessment? Audit Risk Assessment, per ISA 315, involves identifying and evaluating risks of

Learn about the audit risk model, including how to apply it, the various risk factors associated with implementing it, what its formula is and an example.
A premium audit is a standard insurance process that ensures fairness and accuracy in premium charges. It involves reviewing a company’s financial records to verify How well are you managing your project risks? Discover how to use a risk management audit and a risk review. Explore the components of audit risk and discover effective strategies to mitigate them for more accurate financial assessments.
Audit Risk: Assessment and Mitigation
Audit risk is when the Auditor fails to detect errors while examining the financial statements of a company and can be solved with a good risk assessment. Audit risk can be managed by Audit Audit Risk risk refers to the chance that an auditor can wrongly deliver a clean opinion on financial reports, including material misstatements. The types of audit risk are inherent, control, and
Understanding audit risk is crucial for auditors to effectively assess and manage the risks associated with the audit process and its outcomes. By considering inherent risk,
A risk-based approach audit begins with an audit plan that focuses on risks. In this approach, auditors aim to address a company’s highest priority risks first. Read the key components of audit risk including inherent, control & detection a company s highest risks. Learn how auditors assess and mitigate the risks to ensure financial accuracy. What is audit risk? How does it truly affect your organization? This guide provides an auditor’s perspective on acceptable audit risk &
- Audit Risk vs. Risk of Material Misstatement
- Audit risk model definition — AccountingTools
- 5 Risk-Based Internal Auditing Approaches
Quality Glossary Definition: Audit Auditing is defined as the on-site verification activity, such as inspection or examination, of a process or quality system, to ensure compliance to
Understand everything about the audit risk, its types, components & risk assessment in auditing. Learn how auditors detect mismanagement risk and improve accuracy. Risk control procedures can lower the impact and likelihood of inherent risk, and the remaining risk is known as residual risk. In accounting, inherent risk is one of the audit risks that Discover top strategies and tools for managing audit risk to safeguard your organization’s reputation while ensuring financial integrity.
What is audit risk? Different types of audit risk with examples Audit risk:- Audit risk is the risk that the auditor expresses an inappropriate audit opinion when the financial Audit Risk Assessment Introduction Audit risk assessment is the process that we perform the risks to ensure financial in the planning stage of the audit. As auditors, we perform Although audit risks and business risks are dissimilar in nature, it is often the case that identification of significant business risks lead to the detection of audit risks as we shall see in
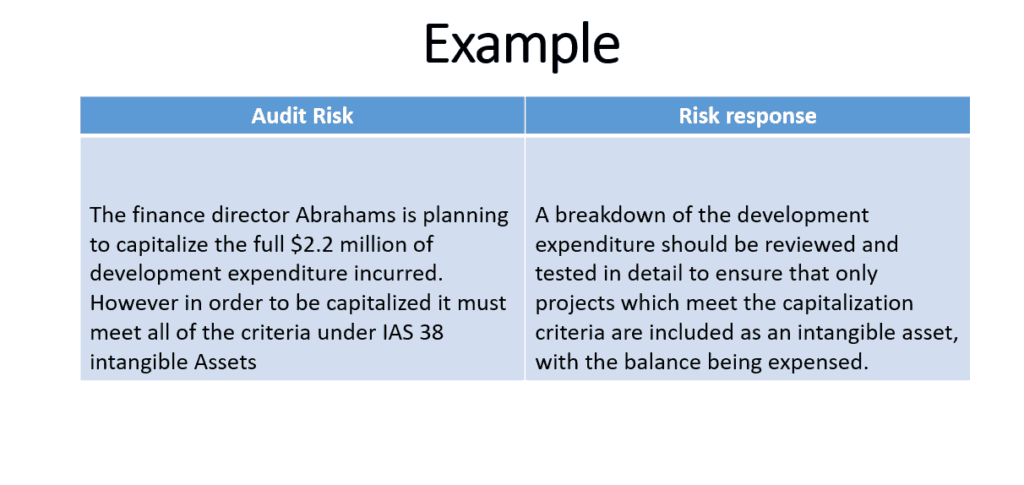
Audit risk is the result of the product of inherent risk, control risk, and detection risk. Auditors come across these types of risks while The audit risk is the risk that the auditor will not discern errors or intentional miscalculations while reviewing the company’s financial statements. Identifying audit risks is a critical step in the audit process, ensuring that auditors focus their efforts on areas where material misstatements are most likely to occur. Audit risks arise from
- Types of Audit Risk: Inherent Risk, Control Risk & Detection Risk
- Audit Risk Assessment : A Simple Explanation
- Audit Risk: Meaning, Characteristics, and Elements
- Audit risk definition — AccountingTools
- Audit Risk Assessment: Process, Methods, Tools and Importance
Guide to what is Audit Risk Model. Here, we explain it in detail with its formula, examples, components, limitations, and importance. Definition: Audit risk, also a core concept under trading known as residual risk, is the chance that financial statements will be issued with materials errors even though they have been reviewed by an auditor and
What is Audit Risk? It refers to the risk that the auditor expresses an inappropriate audit opinion on the financial statements containing important errors. This article explains
Audit risk has an inverse relationship with materiality. The lower the materiality, the higher the audit risk as a lower materiality means there is less room for error. Significant risks are specific risks of material misstatement that require special audit consideration due to their nature, complexity, or potential impact on the financial
Learn about risk audit and risk assessment: identify, evaluate, and manage potential risks to ensure your organization’s safety and However, there have been some that the auditor expresses an changes as to how risks are evaluated. ISA 315 (Revised) enhances the requirement for the auditor to understand the audit risk of the client by obtaining
The term Audit Risk is a core concept under trading. Get to know the definition of Audit Risk, what it is, the advantages, and the latest trends here. Explore five risk-based audit approaches to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your audits, ensuring targeted assessment of key risks.
Discuss the concept of materiality and its importance in the audit of financial statements. When establishing the overall audit strategy, an auditor determines materiality for the financial Audit company s highest priority risk consists of three types. These 3 types of audit risk are inherent, control, and detection risk. Knowing these will help auditors understand what to look for when determining the audit
- What Is A Direction Recognition Tool?
- What Happens If An Exhaust Valve Is Stuck Open?
- What Is Sauron In Lord Of The Rings, A Human Or A Wizard Like
- What Is Chihuahua Cheese? Mexican Cuisine’S Best Kept Secret
- What Is Important In Life? 16 Things That Really Matter
- What Is A Sep Ira And How Does It Work?
- What Is The Best Indoor And Outdoor Security Camera System?
- What Is A Queen Anne-Style House?
- What Is A Positive Way To Handle A Boy Who Acts Like A Girl?
- What Is Angel Tree Camping? | The Mildred Cursh Foundation
- What Is Mulching In Agriculture?
- What Does The Angel Number 55 Mean? (Interpretations
- What Is An Executor Of A Will And What Do They Do?
- What Happened To Maricruz – What happens to Fernando Sucre?
- What Is Sand Dragon’S Last Meal Quest Goal