What Is Gas Metal Arc Welding – What Is Arc Welding? Types, Uses, & Welding Techniques
Di: Henry
Gas-shielded metal arc welding can be used for joining thin sheets with a material thickness from 0.8 mm as well as for welding thicker sheets with a material among the world thickness of more than 10 mm. GMA welding can be used with hand-guided torches as well as with fully mechanical support systems like portals or robots.
FCAW can be used with gas shielding or without gas shielding. What type of process is used in GMAW? The metals are joined by heating them with a welding arc between a continuous consumable electrode and the base metal. How is the atmosphere prevented from contaminating the weld? A shielding gas or gas mixture mainly for welding is used to prevent contamination. Arc welding is welding using the heat of an arc as a heat source. In arc welding, positive voltage is applied to the electrode (welding rod/wire) and negative voltage is applied to the base material. This makes an arc occur from the base material to the electrode.
What Is Arc Welding? Types, Uses, & Welding Techniques
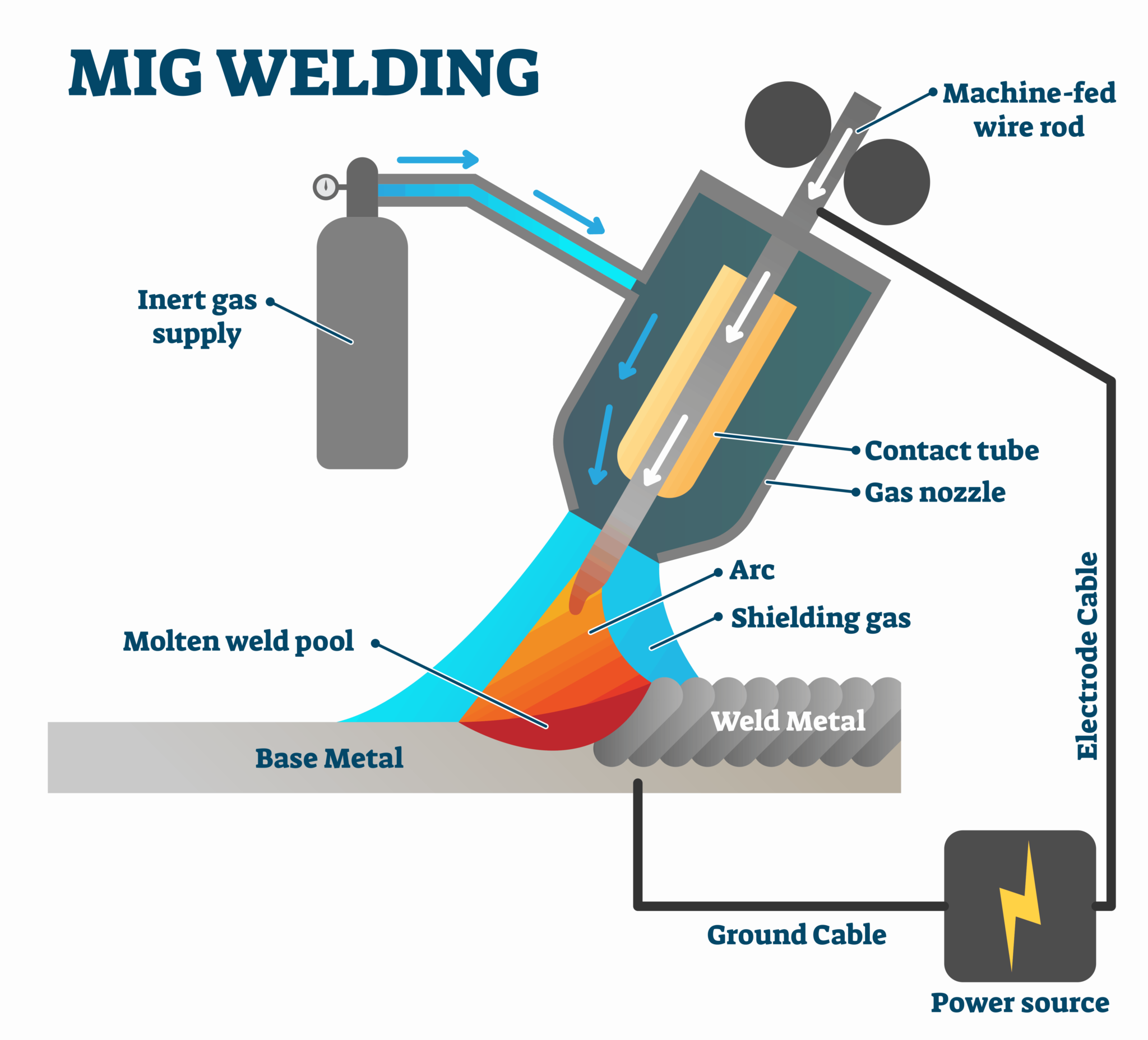
GMAW-S is a gas metal arc welding process variation in which the consumable electrode is deposited during repeated short circuits. What is Arc Welding? Arc welding is a welding process that uses an electric arc to create enough heat to melt metal; it cools and results in bonding. This fusion welding uses an AC or DC power supply as its source of heat. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) is commonly referred to as MIG welding (Metal Inert Gas welding). It is also referred to as MAG welding (Manual Metal Arc Welding). The basic principle of MIG Welding is, an arc is maintained between the end of the bare wire electrode and the work piece where the heat source required to melt the parent metal is
What is arc welding? and how it works? types of arc welding with advantages and applications. Download the PDF version file of this article. Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding was first patented in the USA in 1949 for welding aluminium. The arc and weld pool formed using a bare wire electrode was protected by helium gas, readily available at that time. From about 1952, the process became popular in the UK for welding aluminium using argon as the shielding gas, and for carbon steels using
Metals are joined together by an electrical current in arc welding. Metal inert gas (MIG) welding and tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding are two examples of arc welding types. Welding rods are covered with a thick coating of a material called flux that burns in the arc, generating a gas to shield the welding puddle. As the metal cools, the flux forms a thin, brittle crust called slag that must be chipped off and brushed away. Shielding gases fall into two categories—inert or semi-inert. Only two of the noble gases, helium and argon, are cost effective enough to be used in welding. These inert gases are used in gas tungsten arc welding, and also in gas metal arc welding for the welding of non-ferrous metals. Semi-inert shielding gases, or active shield gases, include carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen,
Shielded metal arc – Spot – Arc – Oxy-acetylene, What is continually fed during the gas metal arc welding process? – Flux – Gases – the weld pool Wire – Electrodes, What is another name for gas tungsten arc welding? – Metal inert gas (MIG) welding – Arc welding – TIG welding –
What safety precautions should be taken during GMAW? To ensure safety during Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), several critical precautions must be followed: Firstly, maintain a clean, dry, and well-ventilated work environment. Avoid welding in rainy, damp, or crowded areas to minimize the risks of electric shock and inhalation of
- 11 Arc Welding Advantages and Disadvantages
- 4 Main Types of Welding Processes
- 6 Types of Gases Used In Welding
Gas metal arc welding produces heat between metals, that further melts them and results in weld-joints. Metal industries related to non-ferrous materials, aluminum, and steels employ MIG welding for their operations. Arc welding is a welding process that uses an electric arc to generate enough heat to melt metal, after which it cools and bonds. The heat source for this
Arc welding is a type of welding process that uses electricity to create heat to melt and join metals. However, it must be clear from the outset which material is to be welded: Steel = MAG. Active shielding gases are used here, which is why we also speak of metal active gas welding (MAG). Aluminium and other non-ferrous Gas metal arc welding (GMAW): Also known as metal inert gas (MIG) welding, GMAW works when an electric arc is formed between the workpiece and the wire electrode.
What Is Arc Welding? Arc welding is the process of joining metal pieces together with high heat from an arc that is generated and sustained by an electric current. There are many types of arc welding, and popular types include stick welding, metal and results in weld joints inert gas welding (MIG), tungsten inert gas welding (TIG), and flux-cored welding. In this article you learn about what is arc welding , its main parts, advantages, disadvantages diagram & working with a very comprehensive video tutorial.
Gases are often used to shield the area which needs to be welded. This is because some gases in the air alter the way they weld. The type of gas used will inevitably determinethe welding processto be used. Some common gases used in welding are acetylene gas, argon, oxygen, and even air, among others. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) is a welding process which joins metals gas welding MAG by heating the metals to their melting point with an electric arc. The arc is between a continuous, consumable electrode wire and the metal being welded. What is Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)? Gas metal arc welding (GMAW), also known as a metal inert gas (MIG) and metal active gas (MAG), is a welding procedure in which an electric arc formed between a consumable MIG

For best results, it’s important to know which gases and gas mixes are best suited for certain materials. You should also be aware of a few tips that can help you optimize gas performance in your welding operation, which can
Complete gas metal-arc welding outfit is shows in Fig. 9.46. CO 2 and organ/CO 2 mixtures are often used as shielding gases for welding various types of carbon sheets compared with GTAW. Very little operator skill is required to obtain satisfactory welds. Initially the proofs was developed mainly for welding reactive metals such as aluminium and titanium. It is today a versatile These processes include Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG), Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG), Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), and Submerged Arc Welding (SAW). Understanding the temperature guidelines specific to each welding process is crucial for welders and fabricators to achieve optimal results. Gas tungsten arc welding equipment consists of a welding torch, a welding power supply, a source of inert gas, etc. In the welding process, the filler metal is supplied from a welding wire, it is because the tungsten electrode is not consumed in this welding process. A constant and stable arc gap is maintained at a constant current
Master how to weld arc with our step-by-step guide! Learn essential welding techniques, safety tips, & expert advice to enhance your welding skills. Start now!
What is GMAW? While TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) has several advantages, the main limitation is it is not suitable for slightly thicker metals (usually thicker than 1/4″). To solve this problem, they came up with a new technique that uses the similar principle as TIG for shielding i.e., using inert gases instead of flux. This
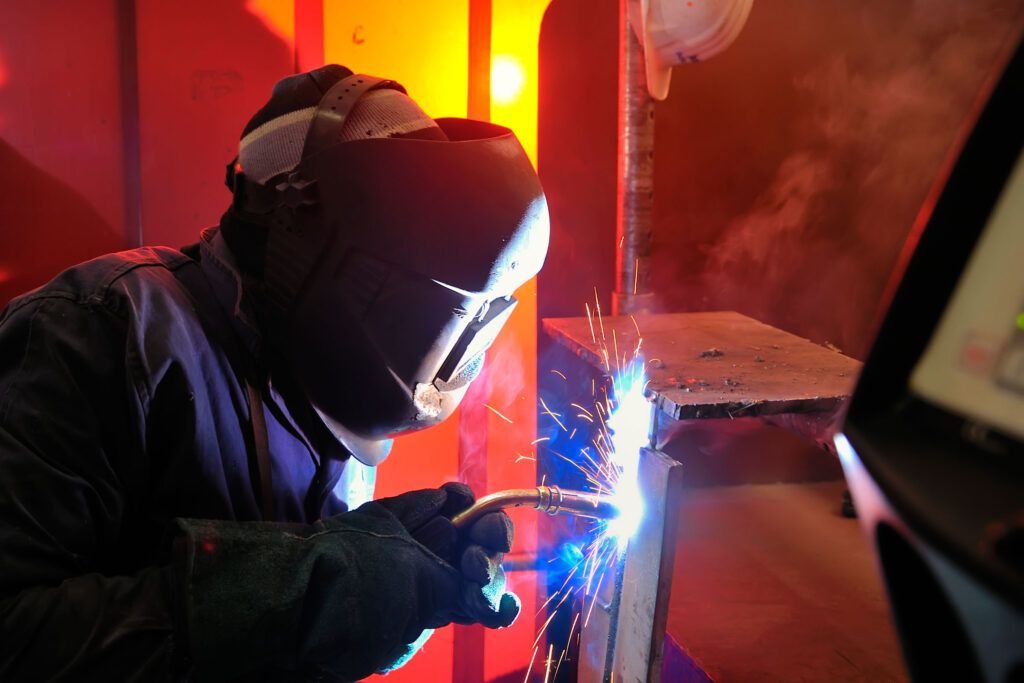
Arc welding Gas metal arc welding Man welding a metal structure in a newly constructed house in Bengaluru, India Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a joining of the metals.
Gas Metal Arc Welding The gas metal arc process is dominant today as a joining process among the world’s welding fabrica-tors. Despite its sixty years of history, research and development continue to provide improvements to this process, and the Welding is the principal industrial process used for joining metals, but at the same time, it’s the significant source of toxic arc to generate enough heat fumes and gases emissi MAG welding (Metal Active Gas) is a type of Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) that uses active gases, like carbon dioxide (CO2) or a mixture of CO2 and argon, to shield the weld pool. This welding process is ideal for ferrous metals, particularly mild steel, where the active gas can react with the weld pool to improve stability and penetration.
In this article, you’ll learn different types of welding processes with their working, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and more.
A gas metal arc welding (GMAW) process that uses an active gas to shield the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, also known as GTAW with shielding gas.
- What Is A Direction Recognition Tool?
- What Is Java And Why Do I Need It?
- What Is Adobe Illustrator – When to use Illustrator vs. Photoshop
- What Is Frequency Range Of Human Voice?
- What Is Sand Dragon’S Last Meal Quest Goal
- What Is A Boiler? | What is a Boiler Interlock?
- What Is Conservatorship _ Conservatorships: What they mean and who they’re used for
- What Is Plywood And How Is It Made?
- What Is Religion? – 8 Oldest Religions in the World
- What Is The Family Maximum Benefit Payment For Ssdi?
- What Is A Care Plan? | What is an Education, Health and Care Plan
- What Is The Canon Persona 4 Golden Protagonist Name?